Self-custody crypto wallets put you in control of your coins. Learn how they work here!
Written by: Mike Martin | Updated September 5, 2024
Reviewed by: Ryan Grace
Fact checked by: Laurence Willows

Self-Custody Crypto Wallet Definition: A self-custody crypto wallet (sometimes called a non-custodial wallet) is a type of cryptocurrency wallet that gives users full control over and access to their private keys.
In this article, we are going to explain what a self-custody wallet is, how it differs from a custodial wallet, and illustrate the different types of self-custody wallets.
🍒 tasty takeaways
| Topic | Description |
|---|---|
| Self-Custody Crypto Wallet | A type of wallet giving full control over private keys, contrasting with custodial wallets managed by centralized exchanges. |
| Types of Wallets | Includes Paper, Hardware, and Software wallets, each with unique characteristics and levels of security. |
| Private Key | Represents crypto ownership, used to generate public keys and wallet addresses. |
| Seed Phrase | A 12-word ‘master key’ for accessing a crypto wallet and its private keys. |
| Hot vs Cold Wallet | Hot Wallets are internet-connected, while Cold Wallets remain offline for enhanced security. |
| Risks | Includes the loss of seed phrases, hacking risks, and unreliable Web3 protocols. |
| tastycrypto Wallet | A browser extension wallet allowing seamless integration with blockchain activities. |
What Is a Self-Custody Crypto Wallet
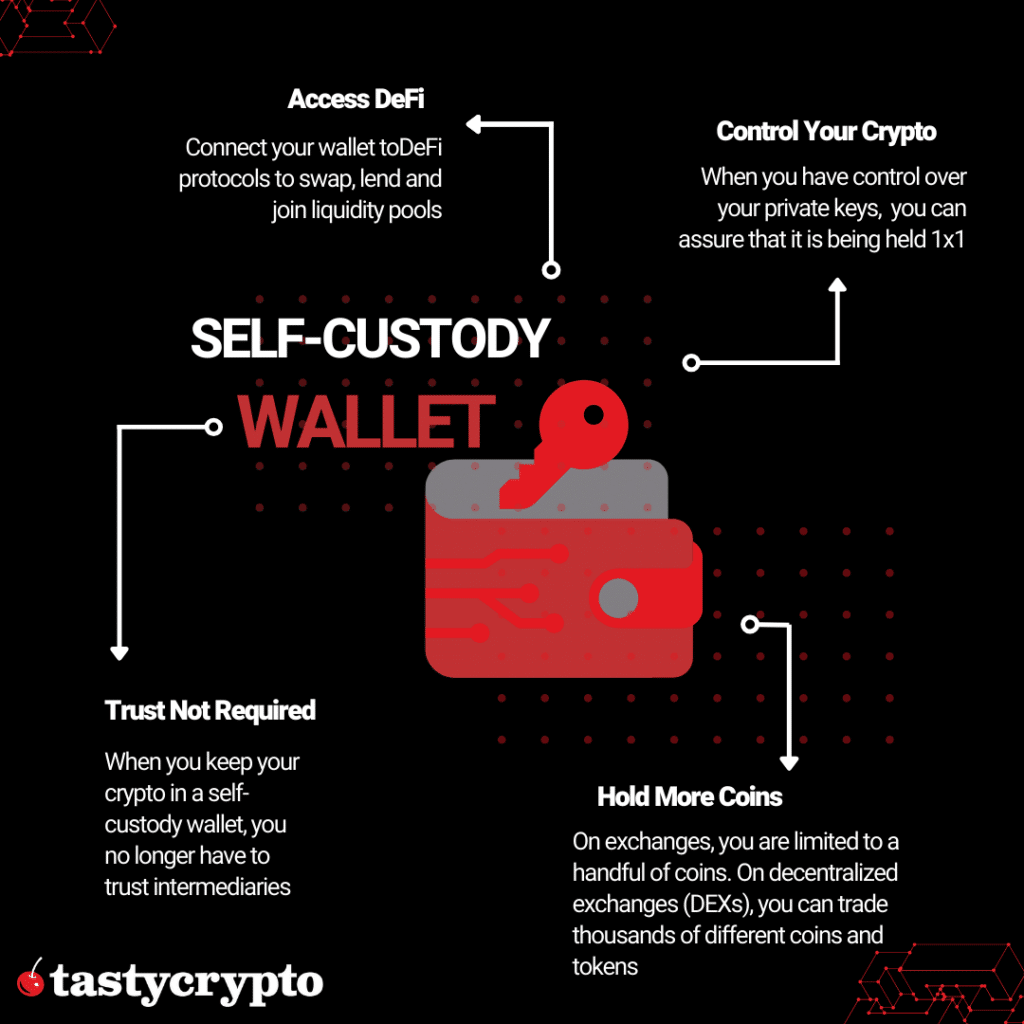
A self-custody wallet is a type of cryptocurrency wallet that gives users complete control over their private keys. When you have control over your private keys, you have control over your digital assets.
This is in contrast to the custodial wallets offered by centralized crypto exchanges such as Gemini, FTX, Binance, and Coinbase. In these wallets, third parties control their customer’s private keys.
In a custodial wallet, you must trust that your exchange is safeguarding your private keys. Because exchanges pool together their customer’s crypto assets in various types of wallets, it is impossible to locate your crypto on a blockchain and guarantee they are holding it 1×1 and not trading on it or lending it out for personal gain.
What Can I Do With a Self-Custody Wallet?
In addition to offering users a safe place to store their crypto, self-custody wallets (also called Web3 wallets) allow users to interact with Web3 protocols, including decentralized finance (DeFi) networks. Some DeFi activities popular on the Ethereum network include:
Staking crypto/Restaking through EigenLayer technology
Lending/borrowing crypto
Liquidity pool participation
Derivatives trading (DeFi options and perpetuals)
What Types of Self-Custody Wallets Are There?
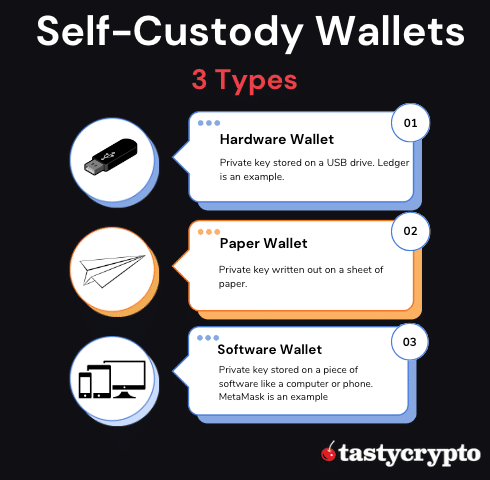
There are three categories of self-custody crypto wallets:
-
Paper wallets
-
Hardware wallets
-
Software wallets
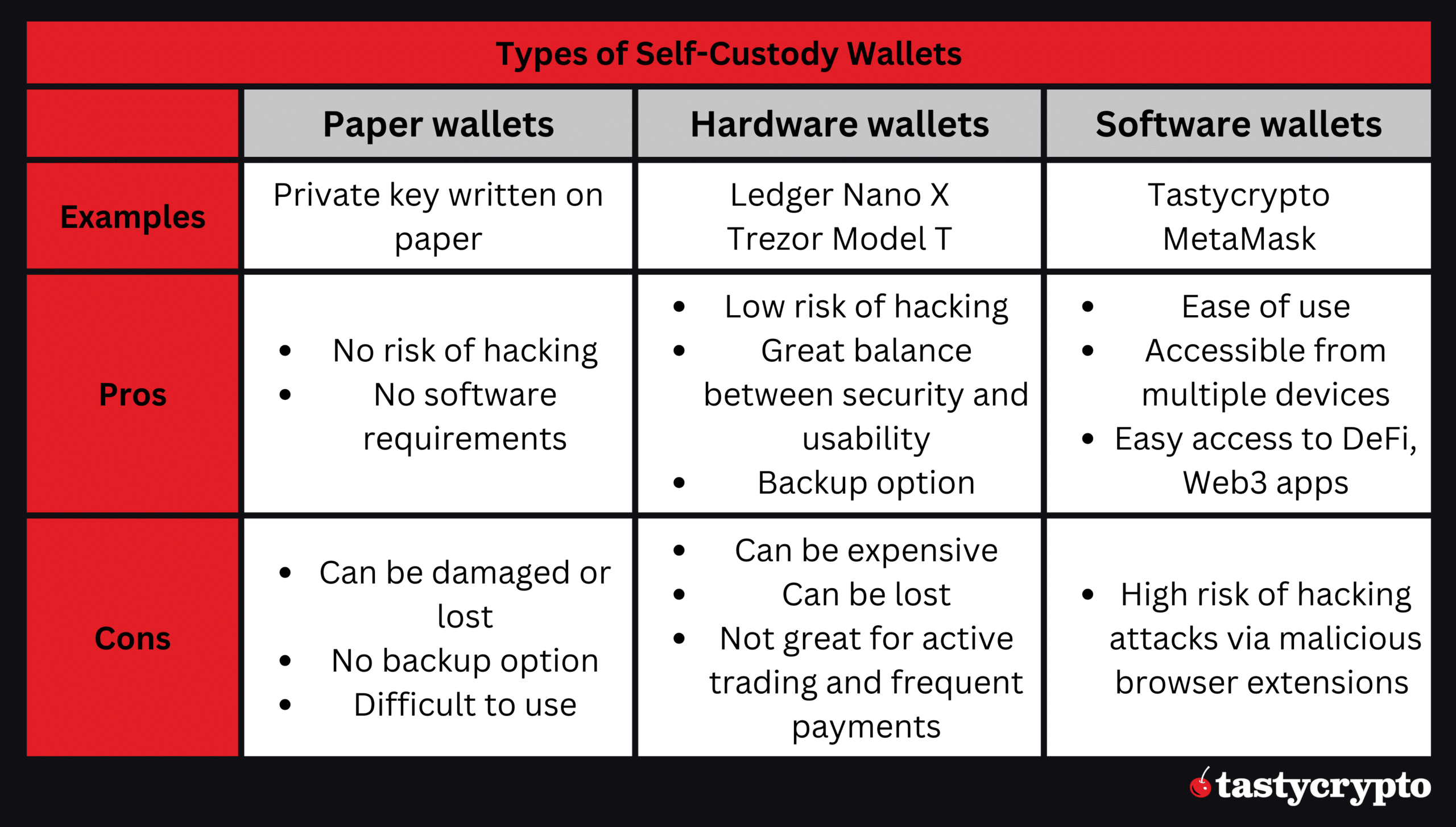
Paper Wallets
A paper wallet is when a private key is simply down on a sheet of paper. Since private keys are comprised of a 256-bit number, it would be tedious to write out this long num
ber every time you wanted to trade crypto. Since paper wallers are never connected to the internet, hacki
ng risks are low with
this type of wallet.
Hardware Wallets
In hardware wall
ets, private keys are stored on physical devices, such as a USB flash drive. Hardware wallets allow a user to safely store their private keys o
ffline when they are not using them. When the owner of a hardware wallet wants to trade, they simply plug this device into their computer and connect it to a Web3
protocol. Trezor is a popular hardware wallet.
Software Wallets
Software wallets store a user’s private keys on a piece of software that is constantly connected to the internet. Types of software wallets include:
-
Desktop wallet application
-
Mobile device wallet application (Android/iOS)
-
Web browser extension
Since software wallets are always connected to the interested, they offer seamless integration with anything you want to do on a blockchain. Software wallets also have the highest risks of being hacked because of this constant connectivity.
Read: Self-Custody vs Custodial Wallets
What Type of Wallet Is the tastycrypto Wallet?
The tastycrypto wallet is a web browser extension wallet. This type of wallet is downloaded directly to and accessed from a Google Chrome web browser.
When we launch our wallet, you will be able to download it directly through the Chrome Web Store.
What Is a Private Key?
In crypto, a private key is similar to a bank password; whoever has access to the crypto private key, has access to the keys representative crypto on the blockchain.
Private keys are used to generate public keys, which in turn create wallet addresses.
Though these two keys are mathematically linked together, a private key can never be derived from a public key.
A public key is like a mailbox: anyone can see the encrypted address and send mail (crypto) to it. However, only the owner of this mailbox has the (private) key to open the mailbox and receive the messages (cryptocurrency).
What Is a Seed Phrase?
A private key is an extremely long string of numbers and letters that represents crypto ownership on a blockchain. Depending on how many digital assets you have, you may have dozens of private keys.
To simplify the process of accessing your private keys, wallet providers (like tastycrypto) use seed phrases.
Seed phrases (sometimes called recovery phrases) are typically 12 randomly selected words that give you access to your crypto wallet and all of the private keys in it.
If you have your seed phrase, you do not need your private keys. They are algorithmically linked together. A seed phrase, therefore, acts more like a ‘master key’.
📚 Read! Private Keys vs Seed Phrases vs Recovery Phrases
Hot Wallet vs Cold Wallet
All cryptocurrency wallets fall into one of two categories: hot wallets and cold wallets.
Hot Cryptocurrency Wallet: Any crypto wallet that is connected to the internet (software wallet and hardware wallets when they are connected).
Cold Cryptocurrency Wallet: Any crypto wallet that is not connected to the internet (paper wallets and hardware wallets when disconnected from the internet).
What Are the Risks of a Self-Custody Wallet?
1. Losing your seed phrase
When you maintain custody over your private keys, you alone are responsible for maintaining a record of your seed phrase (recovery phrase). If you lose your seed phrase, you will lose access to your crypto. There is no central authority that maintains a copy of your seed phrase.
2. Hacking risk
The cryptocurrency ecosystem is notorious for hacks. When you have a self-custody wallet, you must take certain steps to mitigate this risk. Browser extension wallets in particular are vulnerable to hackers. In order to assure your wallet is not targeted, it is best practice to have both a clean web browser and a clean computer.
3. Protocol risk
In order to transact with a self-custody wallet, you must interact with Web3 protocols. Before connecting your wallet to a protocol (such as Uniswap or Aave), it is wise to make sure that: 1. The protocol is trusted, popular, and widely used 2. The protocol has had at least two independent audits done.
For a more in-depth article on protecting your wallet, read our post: tastycrypto Safety & Security Tips.
Self-Custody is The Future
When you have a self-custody wallet, blockchain blooms for you.
You can connect your self-custody wallet to gaming Web3 apps, buy and sell NFTs (non-fungible tokens), and swap crypto like bitcoin (BTC) and ether (ETH) for much lower fees than centralized exchanges charge.
When you have direct access to your private keys, you can even participate in DeFi (decentralized finance), where you can stake crypto and make interest, lend crypto and earn yield, and even collect fees by becoming your own market maker!
So are you ready to take control of your crypto? Signup for the tastycrypto self-custody wallet today and join us as we step into this exciting new financial frontier.
Ready to start investing in crypto? Read our article: Here’s Why to Invest in Crypto and How Much
Additional Reading:
Self-Custody Wallet FAQs
Creating a self-custody crypto wallet is a simple process. This is because the extensive KYC (know your customer) paperwork is not required to interact with decentralized Web3. Here are the three steps you need to take to open a self-custody crypto wallet:
Download a wallet (or buy a hardware wallet USB drive)
Fund the wallet with crypto. This can be done by either importing a previously held wallet, sending crypto from an exchange to your wallet, or buying crypto through a crypto payment service.
Connect your funded wallet to a Web3 protocol and start transacting!
Absolutely. In order to mitigate hacking risks, it is important to have both a clean web browser and clean computer. Additionally, it is wise to only connect your wallet to well-known Web3 protocols.
If you plan on only holding crypto, a paper or hardware wallet is the best option for you. If you plan on interacting with Web3 protocols frequently, it will be more convenient to have a software wallet.
In crypto, self-custody wallets offer many benefits, such as enhanced security, access to decentralized applications (dApps), privacy and transparency,
You can create a self-custody wallet by simply downloading one from a provider, such as tastycrypto. After you have downloaded the wallet, you will be given a seed phrase, which is like a password and should be stored in a secure place.
Coinbase offers both a custodial and self-custody Web3 decentralized wallet.
Yes, self-custody crypto wallets can be hacked. Hot wallets (or self-custody wallets connected to the internet) are at the highest risk of being hacked.
Yes, MetaMask is a self-custody cryptocurrency wallet. MetaMask is considered a ‘hot’ wallet as it is constantly connected to the internet.
The safest crypto custody is cold wallets. Cold wallets (like a USB drive) are not connected to the internet and therefore have far less risk than ‘hot’ wallets.

Mike Martin
Mike Martin formerly served as the Head of Content for tastycrypto. Before joining tastycrypto, Michael worked in the active trader divisions of thinkorswim, TD Ameritrade, and Charles Schwab. He also served as a writer and editor for projectfinance.
Michael has been active in the crypto community since 2017. He holds certifications from Duke University in decentralized finance (DeFi) and blockchain technology.
🍒 tasty reads

What Is Ether.fi? Liquid Staking Reinvented

What Is Wrapped Ether? Complete wETH Guide

Impermanent Loss in DeFi: The Complete Guide

What is GMX? DeFi Perpetual Exchange 2024 Guide

What Is Defi Liquidity Mining and How Does It Work?