Definition: Web3 apps are decentralized applications that leverage Web3 technology.
Written by: Siyu Ren Heinrich | Updated June 14, 2024
Reviewed by: Mike Martin
Fact checked by: Ryan Grace

Web3 Apps are decentralized applications that utilize blockchain technology to achieve benefits such as increased decentralization and privacy. In this article, we explain what they are and present five areas that illustrate what the Internet of tomorrow will look like.
Table of Contents
🍒 tasty takeaways
Web3 has a ‘vision’ for a better internet. It employs new technologies that provide users with various benefits in the areas of privacy, governance, and autonomy.
A key criterion of Web3 is the decentralized and open structure of software, which represents a sharp contrast to the often very centralized Internet of recent years.
Web3 technologies are used in different areas and range from internet browsers to DeFi and Metaverse technology
Summary
| Detail | |
|---|---|
| Definition of Web3 Apps | Web3 apps are decentralized applications that leverage Web3 technology, utilizing blockchain for increased decentralization and privacy. |
| Web3 Vs Web2 | Web3 focuses on decentralized and smart applications with distributed ledgers, unlike Web2 which centralizes dynamic content that reacts to user input. |
| Benefits of Web3 Apps | They offer decentralized ecosystems, privacy and data safety, open access, interoperability, and are often open source. |
| Limitations of Web 3.0 | Development and use of blockchain technologies are new, they require improvement in user experience, and may have performance fluctuations with high user volume. |
| Examples of Web3 Apps | Web3 Browsers like Brave, Decentralized Data Storage like IPFS, Decentralized Crypto Exchanges like Uniswap, Metaverse projects like Decentraland, and DAOs like BitDAO. |
| Web3 Browsers | They are open source, offer ad-blocking functions, eliminate user tracking, focus on security, and users can integrate self-custody crypto wallets with them. |
| DAOs | DAOs are Decentralized Autonomous Organizations where execution of certain processes is dictated by the rules defined in the code, and they cut out the middleman making banks, lawyers, and accountants obsolete. |
Web1 vs Web2 vs Web3
To better understand Web3 Apps, let’s take a quick look at the history and different ‘versions’ of the world wide web:
Web1 was the first iteration of the world wide web’s evolution, lasting approximately from 1990 to the early 2000s. In this phase, users mainly used the internet to look up information. Due to its static nature, it was difficult to create and share data.
Web2 has enabled easy interaction and collaboration between users. Centralized social networks and dynamic content that reacts to user input emerged during this phase.
Web3 focuses on smart applications where users can manage data personally and decentrally with the help of distributed ledgers such as blockchain technology.
5 Benefits of Web3 Apps
Various types of software are referred to as Web3 Apps, Web 3.0, or dApps (decentralized apps). These types of software include blockchain games, decentralized finance (DeFi) applications, and NFT marketplaces. Many functions of Web3 apps are executed on blockchains, usually the Ethereum blockchain. Cryptocurrency is often used as a means of accessing the individual functions of Web3 applications.
📖 Read: What is Cryptocurrency? Beginners Guide
Here are a few examples of how Web3 provides value to users:
Decentralized: The Web3 ecosystem utilizes decentralized blockchain technology. This brings numerous advantages compared to most Web2 equivalents, which tend to be highly centralized and can pose various risks to users.
Privacy and Data Safety: Web3 applications either store important data such as user information decentrally or not at all. This reduces hacks and misuse of personal data, thus much less power is placed in the hands of service providers.
Open To Everyone: Anyone can use the software and access information in Web3 – regardless of location or other criteria.
Interoperability: Many Web2 apps (e.g. social media platforms) put up hurdles to prevent users from using other services. Web3 apps are much more open. The free exchange of data between different applications is made possible by greater compatibility with other software.
Open Source: Many applications are open source. This allows codes, smart contracts, and other elementary components of the applications to be checked independently. In addition, the open codes also allow other users to develop their own solutions, this corresponds to the original open concept of the internet.
Limitations of Web 3.0
As promising as Web 3.0 is, there are also some limitations that we want to outline:
The development and use of blockchain technologies often represent new territory. Accordingly, malfunctions do sometimes occur in the software, which can be exploited by bad actors.
Many Web3 apps still need to improve and offer a better user experience.
Due to the decentralized nature of the applications, performance fluctuations can occur with too many users. Scalability is a known problem in the crypto space and various solutions are being worked on, such as the various Layer 1 and Layer 2 scaling solutions on Ethereum and other blockchains like Arbitrum, Optimism, and Polygon.
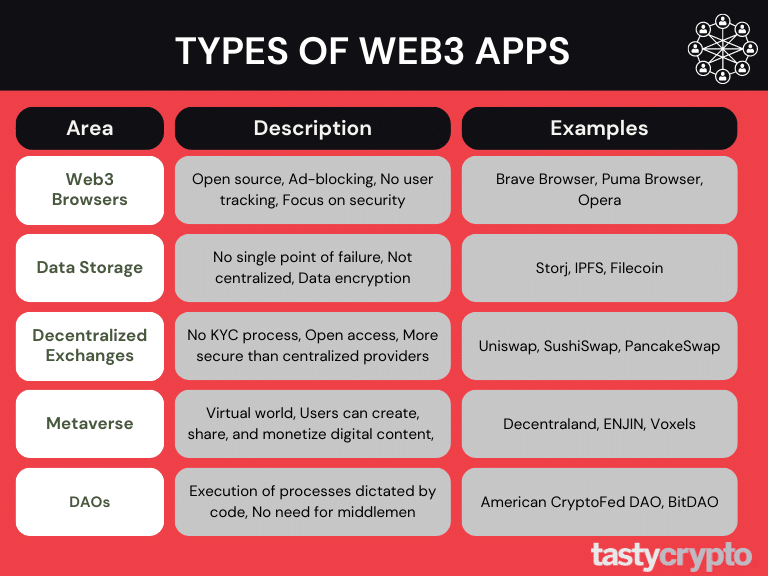
5 Types of Web3 Apps
1. Web3 Browsers
Many web browsers such as Chrome clutter their users’ screens with advertising and at the same time try to collect as much information as possible about user behavior. Web3 Browsers aim to change that. Depending on the software, they offer various advantages over conventional browsers:
Web3 browsers are open source.
They offer ad-blocking functions and pay users for viewing them.
Many Web3 Browsers eliminate user tracking.
Web3 browsers focus on security.
Users can integrate self-custody crypto wallets such as the tastycrypto wallet or Metamask with the browser.
Users can choose to view ads, and get paid if they do!
Examples of Web3 Browsers are Brave Browser, Puma Browser, and Opera.
2. Decentralized Data Storage
Data Storage in the age of Web 3.0 can be best described as decentralized cloud storage. Details such as pricing, available space, and the technical solutions used by the individual services vary greatly. Here are some ways Web3 storage differs from traditional online data storage:
No single point of failure by distributing data to multiple nodes around the world.
Web3 apps are not centralized which means user data cannot be manipulated or abused.
Encryption of all uploaded data increases user privacy and safety.
Examples of Web3 data storage are Storj, IPFS, and Filecoin.
3. Decentralized Crypto Exchanges
Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) are an essential component of DeFi (decentralized finance). They introduce liquidity into the DeFi space via automated market makers (AMMs) and liquidity pools.
DEXs offer many advantages over TradFi services:
No KYC (know your customer) process means that the users’ privacy is preserved.
Open access to the platforms means that no one can be excluded from using them.
Since no single entity is in control of the platform, DEXs are more secure than centralized providers. However, this does not exclude risks such as faulty codes.
Examples are Uniswap, SushiSwap, and PancakeSwap. Check out our in-depth DEX comparison to learn more about their individual pros and cons.
4. The Metaverse
Parts of the metaverse are built using Web 3.0 technology. The metaverse is a virtual world that allows users to create, share, and monetize digital content. In connection with blockchain technology, there is also a lot of overlap between decentralized gaming and NFTs (non-fungible tokens). Since there are numerous providers and projects in this area, the applied technologies, models for governance, and economics are also different.
Examples of Metaverses include Decentraland, ENJIN, and Voxels.
5. DAOs
The term DAO stands for Decentralized Autonomous Organization. It is a group or company that is bound by the rules of code which usually are executed as smart contracts on a blockchain. The Bitcoin network is considered to be one of the earliest DAO. Here is what makes DAOs special:
The execution of certain processes is dictated by the rules defined in the code. The rules of the DAO cannot be changed by individuals but only collectively.
Important decisions such as changing the DAO network’s algorithm can only be made collectively. Unlike most other organizations, no central authority can provide direction.
Due to their structure, DAOs cut out the middleman – making banks, lawyers, and accountants obsolete.
Examples of DAOs are the American CryptoFed DAO and BitDAO.
FAQs
DappRadar is currently tracking over 14,300 different Web3 Apps that are blockchain-based in one way or another. In addition, there are other areas such as artificial intelligence that also use Web3 technologies. Currently, the Ethereum blockchain hosts most Web3 Apps.
Web3 development is still in its infancy. Nevertheless, the first approaches are very promising. Accordingly, an investment can be worthwhile. Check out our guide about how to invest in Web3 in 2023 if you want to learn more about some promising possibilities.
Web3 Apps are developed by thousands of startups and developers worldwide. As with the development of blockchain and crypto technologies, new innovations are constantly emerging. The coming years will show which solutions and services are going to ultimately prevail.
There are many other promising Web3 Applications built on decentralized networks, such as messaging apps, video streaming platforms, prediction markets, borrowing and lending, etc.
Web3 has also been integrated into supply chain management and logistics in order to increase transparency and reduce costs.

Siyu Ren Heinrich
5 years of experience in crypto research of writing practical blockchain and crypto analysis on Medium.
MSc in Computer Science, BSc in Smart Engineering, and BSc in Economics and Statistics.
Michael has been active in the crypto community since 2017. He holds certifications from Duke University in decentralized finance (DeFi) and blockchain technology.
🍒 tasty reads


Aerodrome (AERO) For Beginners: The Ultimate 2024 Guide


Here’s How DEXTools (DEXT) Works in 2024

What Is Jasmy Coin and How Does It Work in 2024?


