Hot wallets and cold wallets serve as two separate forms of self-custody for digital currencies. Cold wallets are offline storage solutions, like USB drives, which are not connected to the internet. Hot wallets are connected to the internet and include browser extensions and mobile apps.
Written by: Anatol Antonovici | Updated January 2, 2024
Reviewed by: Mike Martin
Fact checked by: Ryan Grace
Table of Contents
🍒 tasty takeaways
Self-custody wallets securely store private keys without sharing them with third parties.
Hot wallets require an internet connection, offering easy access to decentralized finance (DeFi) and Web3 apps.
Cold wallets store private keys offline, providing the highest possible level of security.
Summary
| Feature | Hot Wallets | Cold Wallets |
|---|---|---|
| Connectivity | Internet required | No internet, offline use |
| Security | Less secure, vulnerable to online threats | Most secure, immune to online hacks |
| Usage | Convenient for active trading and payments | Best for long-term storage |
| Cost | Most are free | May require initial purchase (e.g., hardware wallets) |
| DeFi Access | Direct access to DeFi platforms | Limited or no direct DeFi platform access |
| Private Key Control | User maintains private key | User maintains private key |
What Is a Self-Custody Wallet?
A self-custody wallet, also called a non-custodial or Web3 wallet, is a cryptocurrency wallet that holds your private keys, giving you full control over stored digital assets like Bitcoin or Ethereum. Self-custody wallets enable peer-to-peer (P2P) crypto transactions and can connect directly with smart contracts, giving access to DeFi applications.
Self-custody wallets, unlike those from centralized exchanges, keep private keys solely with the user and often don’t require registration or KYC verification.
Crypto Hot Wallet vs. Cold Wallet
Self-custody wallets, also called decentralized wallets, safeguard private keys. There are two primary types of self-custody wallets:
- Hot wallets are connected to the Internet and can be used for regular on-chain transactions, such as interacting with DeFi apps or sending payments. They come in the form of browser extensions, desktop apps, or mobile apps. Centralized exchange wallets also fall into the category of hot wallets, but they don’t provide self-custody, so we’re not discussing them in this article.
- Cold wallets store crypto funds entirely offline. They may come in the form of hardware or even paper. Hardware wallets store digital assets offline, but they can easily connect to the Internet through a USB port. Still, cold wallets are more suitable for long-term storage.
Both wallet types offer enhanced security over custodial wallet apps by storing private keys, with cold wallets generally being more secure.
Hot Wallet Pros and Cons
Let’s now compare some advantages and disadvantages of hot wallets.
| Hot Wallet Pros | Hot Wallet Cons |
|---|---|
| User-friendly desktop/mobile apps. | Exposure to online security threats. |
| Easy DeFi and Web3 app access. | Need for careful seed phrase storage. |
| Features like in-app swaps and staking. | Risk of smart contract vulnerabilities. |
| Tracks transactions, balances, NFTs. | Can be less private than cold wallets. |
| Mostly free and easy to set up. | May lead to impulsive or less thoughtful transactions. |
Examples of Hot Wallets
One of the best non-custodial hot wallets is the wallet application provided by tastycrypto. It is available as a browser extension or mobile app (iOS and Android). tastycrypto gives you full control over your crypto funds and focuses on user experience by offering extra features, such as token swaps, NFT support, and DeFi integration.
tastycrypto offers both iOS and Android self-custody wallets – download yours today! 👇
Other popular hot wallets include MetaMask, Trust Wallet, and Coinbase Wallet.
Cold Wallet Pros and Cons
Here are a few reasons to use (and not use) a cold wallet:
| Cold Wallet Pros | Cold Wallet Cons |
|---|---|
| Top security with offline private keys. | Costs of physical devices (between $50 and $200). |
| Higher degree of privacy. | Less convenient for frequent transactions. |
| Ideal for long-term storage. | Not as user-friendly for beginners. |
| Freedom from regular updates or emerging security issues. | Potential risk in case of physical damage or loss. |
| Resilient against online attacks and social engineering. | Limited or no access to DeFi applications directly. |
Examples of Cold Wallets
There are several types of cold wallets, including hardware and paper wallets. Hardware devices, such as the ones provided by Ledger and Trezor, are the most popular options.

Source: Ledger
A highly secure option to securely store your seed phrase is a metal backup storage solution provided by Cryptosteel.
Source: Cryptosteel
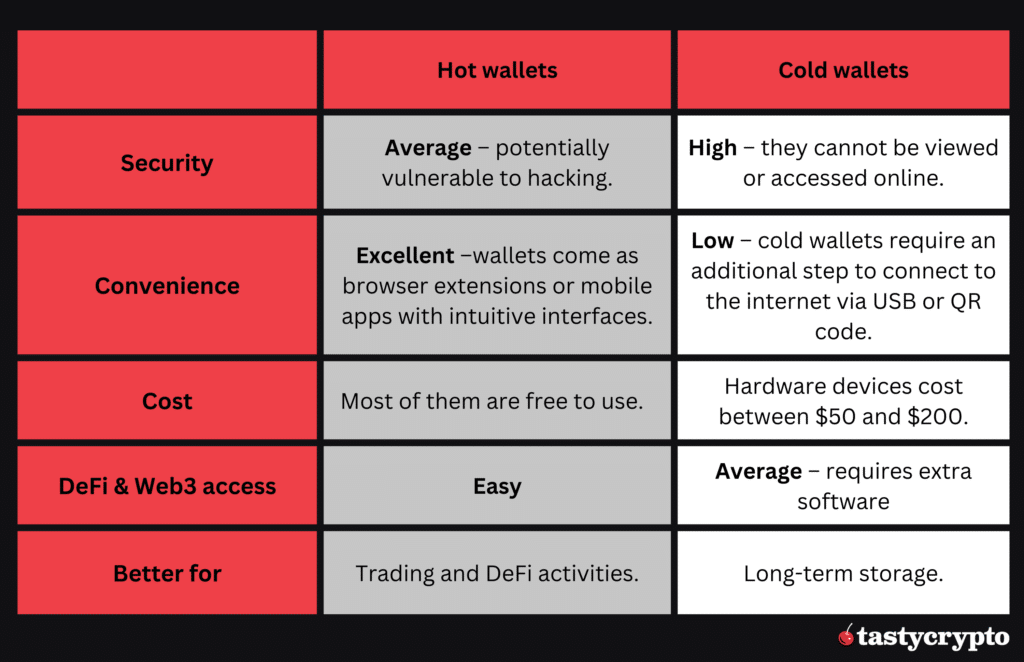
Hot Wallets vs. Cold Wallets: Comparison
When choosing between a hot or cold wallet, you should consider the following factors:
- Security – cold wallets, which store private keys offline, are highly secure. However, certain types, such as hardware wallets, provide access to DeFi apps, which can introduce potential security vulnerabilities, as evidenced in the Ledger incident. Hot wallets are less secure due to their exposure to smart contract vulnerabilities and social engineering schemes – which are necessary evils to interact with DeFi apps.
- Convenience – cold wallets are less convenient than hot wallets, as they require multiple steps to connect online and conduct cryptocurrency transactions on decentralized exchanges (DEXs). Some hot wallets provide multiple features to swap tokens and stake coins directly from the app, which makes the whole Web3 experience more convenient.
- Cost – cold wallets come with a higher cost, as basic models start at around $50. In contrast, hot wallets are mostly free.
- DeFi interaction – hot wallets lead in DeFi and Web3 compatibility, offering features like cross-chain swaps, NFT support, and DeFi integration. Cold wallets, prioritizing security, generally lack these functionalities, making them less ideal for active engagement in DeFi.
- Use Cases – hot wallets are more suitable for an active DeFi experience, while cold wallets are ideal for long-term crypto storage.
FAQs
A self-custody wallet is a type of crypto wallet that grants users complete control over their crypto assets by holding their private keys. These wallets enable P2P transactions and act as a gateway to the decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystem.
A hot wallet with self-custody is a digital wallet connected to the internet. It may come in the form of a browser extension, desktop app, or mobile app. Such wallets are suitable for regular transactions and DeFi operations.
A cold wallet is an offline self-custody wallet, usually a hardware device or paper wallet, used mainly for long-term storage of crypto assets, offering the highest level of security.
The choice depends on your needs: cold wallets offer higher security for long-term crypto storage, while hot wallets are associated with convenience and user-friendly access to DeFi and Web3 apps.
🍒 tasty reads


The Core Blockchain and DeFi Ecosystem: What You Need to Know

7 Best DePIN Crypto Projects

What Is Symbiotic and How Does It Work in 2024?

Ethereum vs Ethereum ETFs – 5 Major Differences


Anatol Antonovici
6+ years of experience writing for crypto brands and blockchain firms, including Coindesk, Cointelegraph, Bitcoinist, CryptoPotato, Algorand, and OTCTrade.com