Core is a layer 1 blockchain that combines key elements from Bitcoin and Ethereum in an effort to solve the blockchain trilemma.
Written by: Anatol Antonovici | Updated August 26, 2024
Fact checked by: Ryan Grace
Since its launch in January 2023, Core has been making waves with its innovative Satoshi Plus consensus mechanism and growing presence in decentralized finance (DeFi). Dive in to learn how Core is shaping the future of Web3 and DeFi.
Table of Contents
🍒 tasty takeaways
- Core is a relatively new blockchain network that merges elements from Bitcoin and Ethereum.
- It allows Bitcoin miners and BTC holders to contribute to Core and earn rewards in the native CORE token.
- Core has become a major player in DeFi, with its TVL starting to surge in Q3 2024.
Core Chain Supported dApps
| dApp | Details |
|---|---|
| Pell Network | Pell is a multi-chain restaking protocol for Bitcoin, like EigenLayer. It supports 11 chains, with Core rapidly reaching $150 million TVL, making up 50% of Pell’s $320 million total. |
| Colend Protocol | Colend, Core’s leading lending app, reached a peak TVL of $180 million on August 16, now at $117 million. It facilitates direct borrowing and lending on Core. Combined with Pell, it represents 90% of Core’s DeFi TVL. |
| COREx Network | COREx, Core’s top decentralized exchange, hit a TVL of over $10 million on August 21, doubling in value in under two weeks. It supports trading of assets like BTC, WCORE, and USDT. |
What Is Core Blockchain?
Core is a layer 1 blockchain that is compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) and borrows the security of Bitcoin.
Launched in January 2023, Core is one of the most recent layer 1 chains. It proposes a new approach by merging elements from several established chains, aiming to achieve robust security and high scalability while enabling the creation of decentralized apps (dapps) on top of it.
The network is managed by the Core DAO, where holders of the native CORE coin can participate in governance by voting on proposals.
Besides governance, CORE acts as a utility token, used to pay transaction fees and staked to maintain the network’s security.
What Does Core Aim to Achieve?
Core’s main goal is to address the blockchain trilemma by achieving all three key elements of a decentralized network – security, decentralization, and scalability – without compromising any of it.
This difficult task was also the declared mission of older chains like Algorand (ALGO) and Avalanche (AVAX). However, Core proposes a unique approach by combining key elements of major blockchains.
How Does Core Chain Work?
Core promotes itself as the first Bitcoin-aligned EVM-compatible chain. It aims to unlock the potential of Bitcoin in the decentralized finance (DeFi) sector, expanding its robust security to Web3 dapps.
The blockchain uses an innovative consensus mechanism called Satoshi Plus. It merges Delegated Proof of Work (DPoW), Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), and non-custodial Bitcoin staking. By leveraging the hash power of Bitcoin miners while supporting stake-based voting, Core proposes a hybrid consensus algorithm that is energy-efficient and scalable. Here is how the Satoshi Plus consensus combines the three elements:
- DPoW – this component enables BTC miners to recycle their hash power to participate in the security of Core. They can delegate their hashing power to Core Validators, earning additional rewards in CORE tokens.
- DPoS – CORE holders can stake their tokens with Core Validators, having a say in the network’s governance and earning rewards.
- Non-custodial Bitcoin Staking – this feature enables Bitcoin holders to stake their BTC directly on the chain without transferring the ownership of their coins, thus having full control while staking.
Therefore, Bitcoin holders, CORE holders, and Bitcoin miners can contribute to the Core chain and earn rewards.
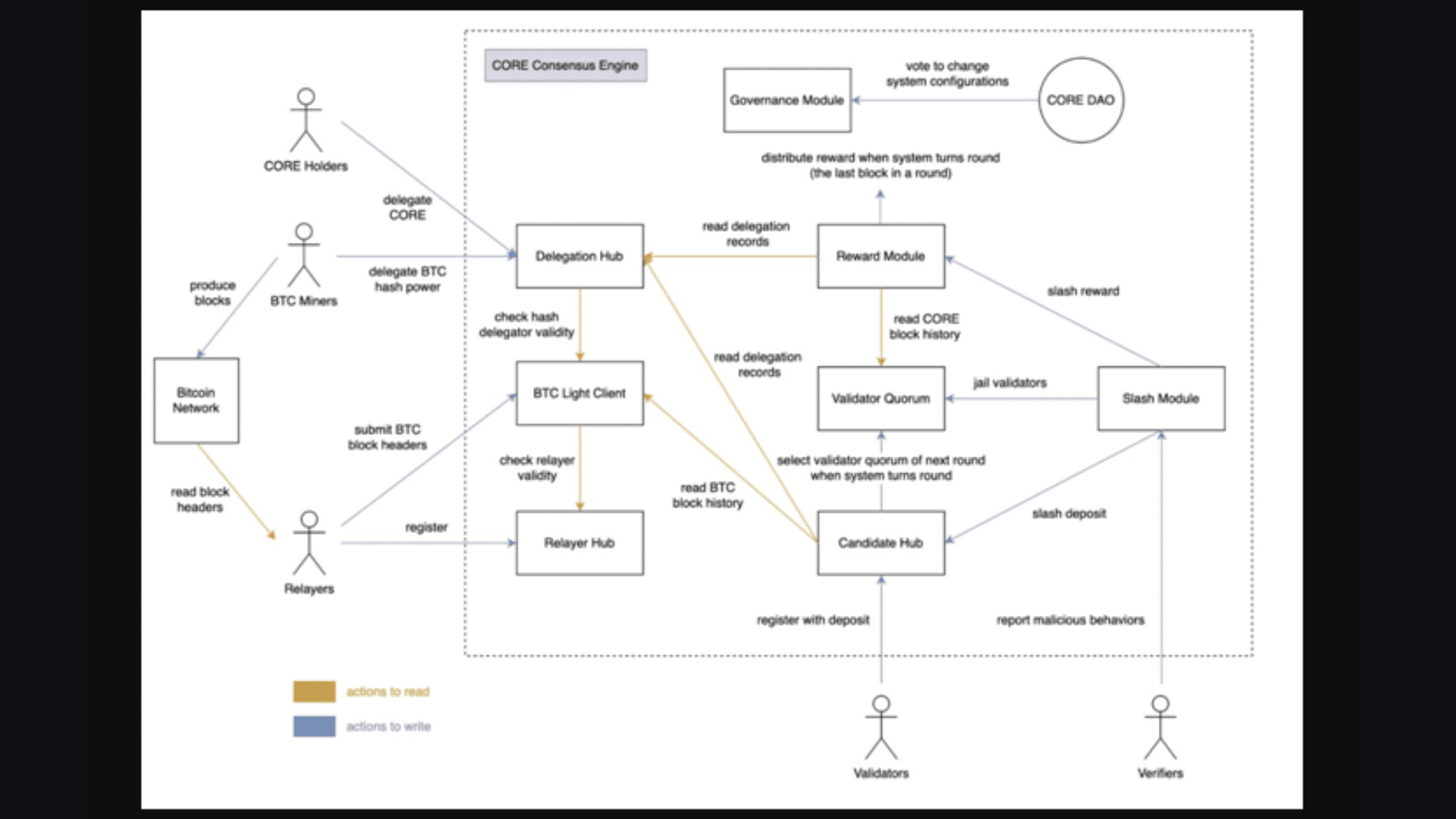
Core Stakeholders
The Core network has several key players, including:
- Validators – they are responsible for generating new blocks on the Core chain. Every 200 blocks, 23 validators are elected based on a hybrid score that reflects their Bitcoin hash power delegated to them and the CORE staked for them.
- Relayers – they share relevant Bitcoin info with the Core network, contributing to the security of the DPoW component. Relayers have to register and stake CORE.
- BTC miners – while securing Bitcoin, miners can delegate their hash power to Core validators.
- CORE holders – they can stake CORE by delegating to validators, thus influencing the validator election process.
- BTC holders – they can stake BTC on the Core chain and then delegate it to a validator of their choice to earn CORE tokens as rewards.
- Verifiers – they are tasked with identifying and reporting malicious behaviors within the Core network.
While this may seem complex at first, this diagram shows how these players interact within the Core network, reflecting the alignment with Bitcoin:
Source: X
CORE Token
CORE serves as the governance and utility token of the Core chain. While it’s technically a coin, the Core team itself is referring to it as a token.
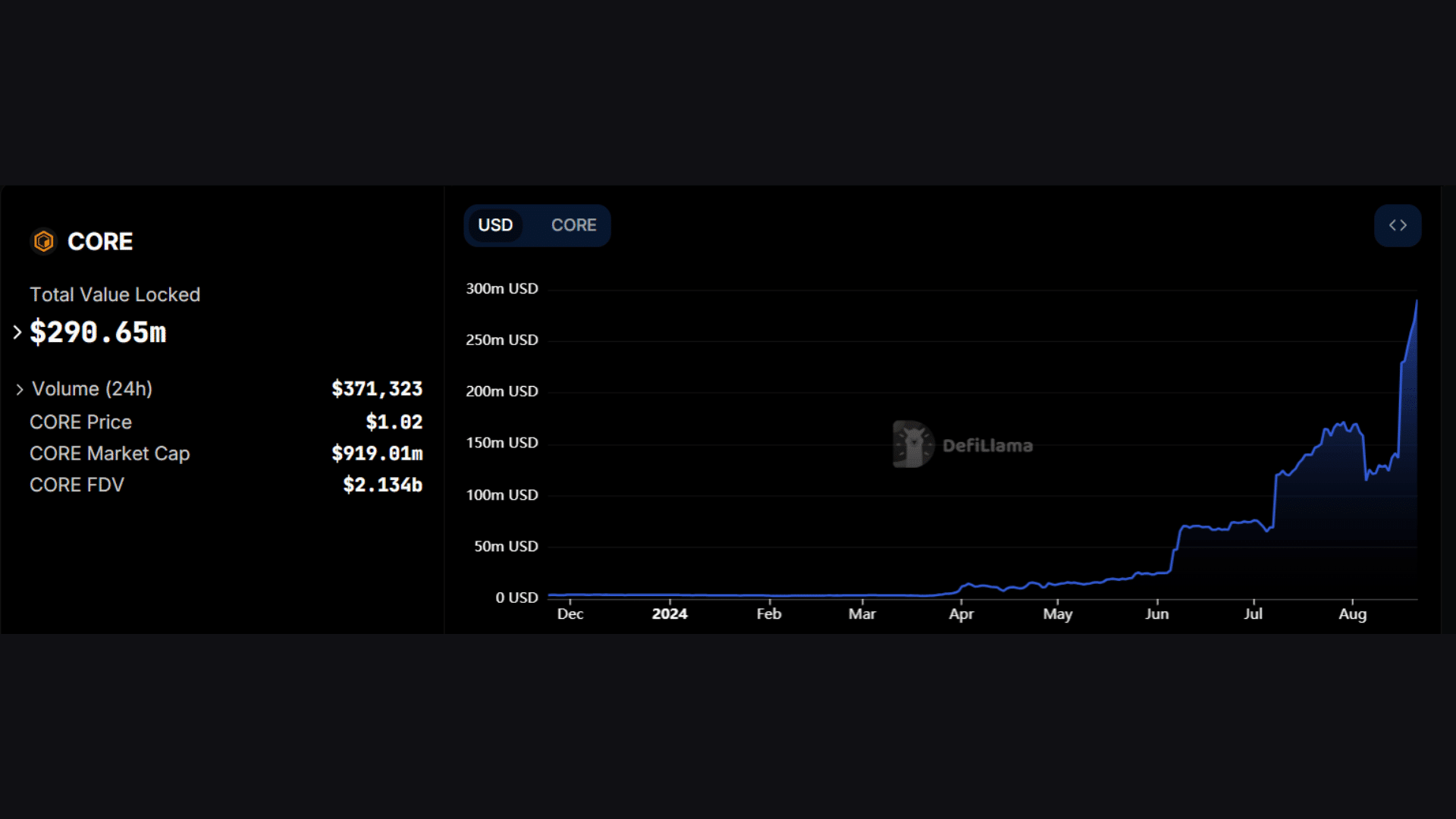
As of August 21, the cryptocurrency is priced at $1.02, having a market cap of $924 million. It ranks 69th on Coinmarketcap. Like Bitcoin, Core has a limited supply, although it’s capped at 2.1 billion. The current circulating supply represents 43% of it.
The CORE price reached an all-time high of $3.7 at the beginning of April 2024. While it has lost over 70% since then, it has still outperformed Bitcoin since the beginning of the year, as shown by this tradingview chart:
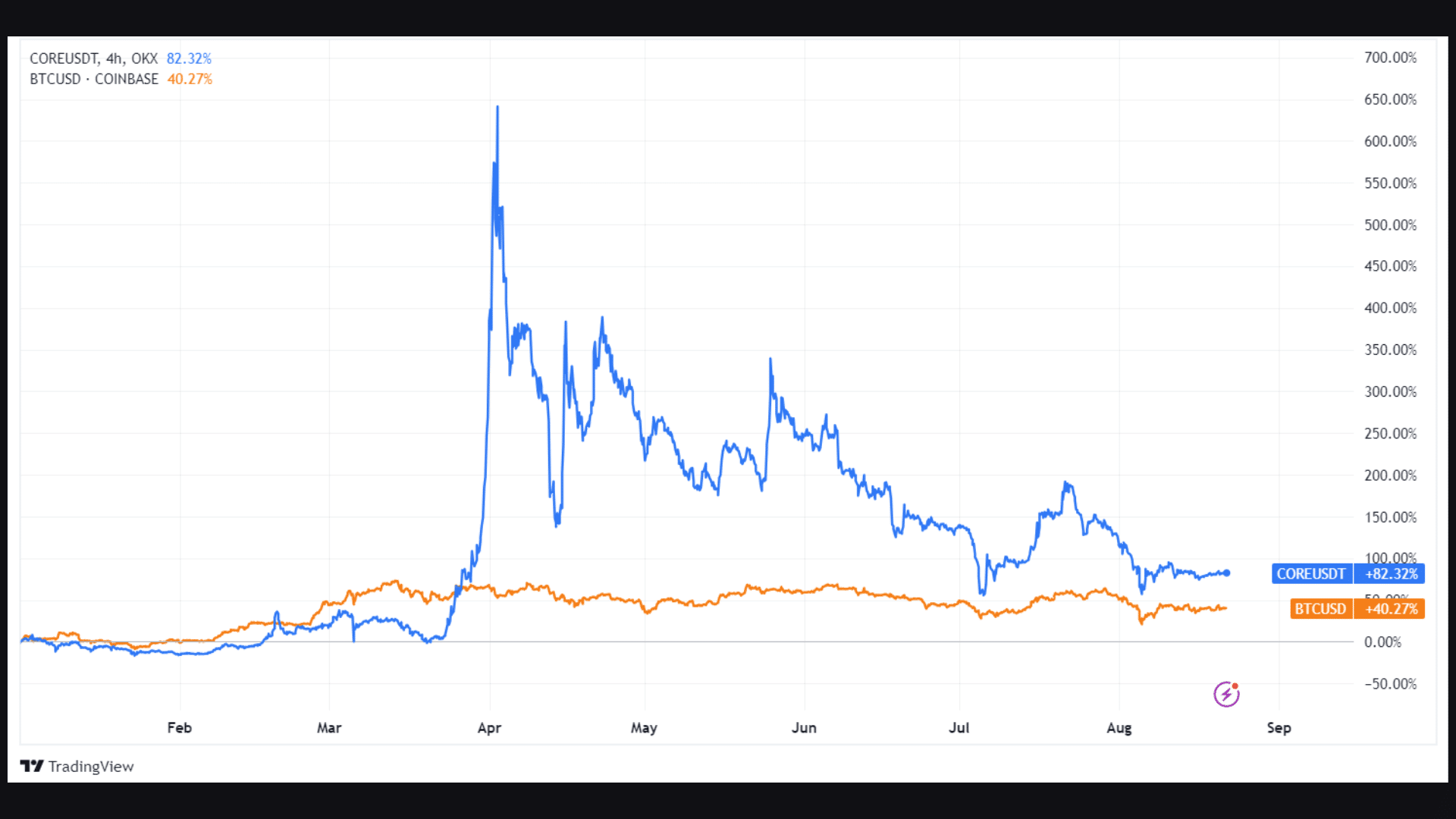
Source: DefiLlama
Core in DeFi
Thanks to its EVM compatibility, the Core chain supports smart contract functionality, being able to host dapps and tokens, including non-fungible tokens (NFTs).
This has helped Core become a major player in DeFi. Its total value locked (TVL) is at a record $290 million as of this writing.
Source: DefiLlama
Here are the main dapps driving Core’s DeFi activity:
Pell Network
Pell is a multi-chain restaking protocol. If you’re familiar with EigenLayer, you should know that Pell works similarly, but it is focused on the Bitcoin ecosystem instead of Ethereum.
It supports a total of 11 chains, including Core, Bitlayer, BSquared, Merlin, and BounceBit. Core has quickly become the leading chain on Pell, with its TVL surging from zero to almost $150 million in less than a month. Therefore, Core accounts for almost 50% of Pell’s total $320 in TVL.
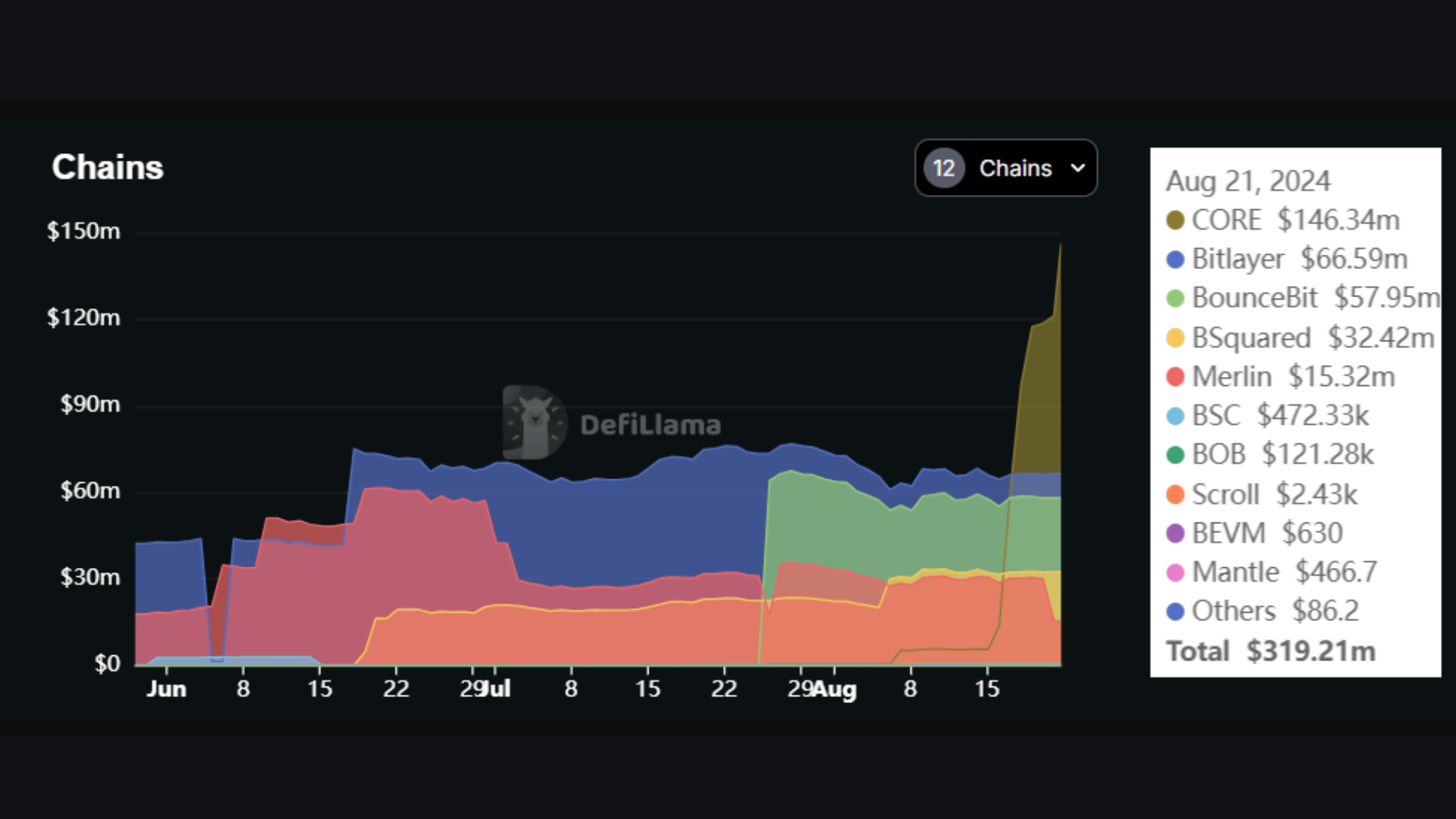
Source: DefiLlama
Colend Protocol
Colend is the main lending dapp on Core. On August 16, its TVL hit a record $180 million before correcting to the current level of $117 million.
The app enables users to borrow and lend directly on the Core chain.
Pell and Colend account for 90% of Core’s TVL in DeFi.
COREx Network
COREx is the main decentralized exchange (DEX) platform on Core, facilitating the exchange between digital assets like BTC, SolvBTC, WCORE, USDC, and USDT, among others.
On August 21, the DEX’s TVL broke the $10 million mark after gaining 100% within less than two weeks.
FAQs
What is Core Blockchain?
Core is a layer 1 chain launched at the beginning of 2023. It combines Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) compatibility with Bitcoin‘s security to support decentralized applications. The network is governed by the Core DAO, with its native CORE token used for governance, transaction fees, and staking.
How does Core work?
Core operates on a consensus mechanism called Satoshi Plus, which combines Delegated Proof of Work (DPoW), Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), and non-custodial Bitcoin staking to achieve security and scalability. This system enables Bitcoin (BTC) miners, CORE token holders, and BTC holders to collectively secure the network and earn rewards.
What are the main DeFi apps on Core?
The main DeFi apps on Core include Pell Network, a multi-chain restaking protocol, Colend Protocol, a lending platform, and COREx Network, a decentralized exchange (DEX).
How to buy CORE?
CORE is available for purchase on major centralized crypto exchanges, including Coinbase, OKX, and Gate.io. While it can be stored on a self-custody wallet like MetaMask, the token is not supported by any decentralized exchange (DEX) at the moment.
🍒 tasty reads


The Core Blockchain and DeFi Ecosystem: What You Need to Know

7 Best DePIN Crypto Projects

What Is Symbiotic and How Does It Work in 2024?

Ethereum vs Ethereum ETFs – 5 Major Differences