Definition: In decentralized finance, liquid staking refers to the process of staking crypto on a protocol and using these staked digital assets as collateral on other decentralized applications.
Written by: Mike Martin | Updated June 28, 2024
Reviewed by: Ryan Grace
Fact checked by: Laurence Willows

The Ethereum Shanghai upgrade, also known as Shapella, has brought staking into the limelight once again. There is also a relatively new type of staking called DeFi liquid staking that is rapidly gaining popularity.
In this article, we describe the unique features of liquid staking.
🍒 tasty takeaways
Unlike normal staking, liquid staking makes your staked digital assets liquid, allowing you to use them for other purposes.
Most DeFi liquid staking protocols use the Ethereum blockchain.
Since the introduction of liquid staking in 2021, the use of these DeFi protocols has steadily increased.
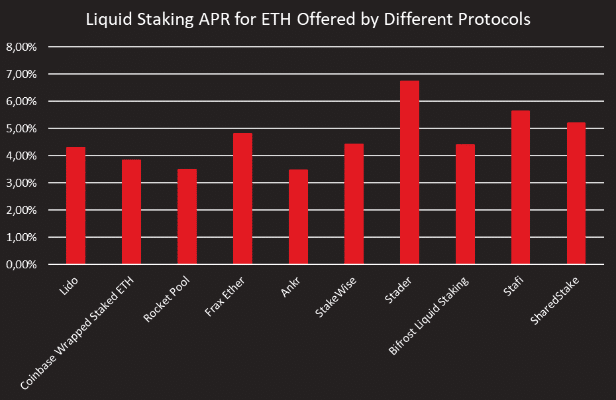
In addition to the security of the respective protocols, the APR (annual percentage rate) is also of essential importance for users. In DeFi liquid staking, these rates currently range from around 3.5% to almost 7%.
New to staking? Check out our guide: What Is Crypto Staking and How Does it Work?
Liquid Staking Summary
| Details | |
|---|---|
| Definition | Staking crypto on a protocol & using staked assets as collateral on other decentralized apps. |
| Unique Feature | Liquid staking allows trading & use of staked crypto assets while earning rewards. |
| Working Mechanism | Users connect wallets to DeFi liquid staking protocol, stake crypto, and receive liquid staking token pegged 1:1 to the asset. |
| Advantages | Utilizes liquidity, no minimum staking amount, no "unbonding period", real-time reward payouts, no infrastructure setup, & additional earnings via derivative tokens. |
| Risks | Derivative token price risk, loss of token, smart contract security, slashing risk, and low adoption threats. |
What Is Liquid Staking?
In traditional proof of stake, users lock up their crypto assets in order to verify and validate network transactions. This makes their staked crypto illiquid. In such cases, users cannot trade, transact or lend their cryptos. Liquid staking, on the other hand, allows users to trade and use their crypto assets while staking.
📖 Read! 5 Different Ways to Stake Your Ethereum
How Does Liquid Staking Work?
The process of liquid staking is quite simple:
First, users need to connect their crypto wallets to a decentralized finance (DeFi) liquid staking protocol.
Users then decide on the amount of crypto they want to stake.
Stakers receive a liquid staking token minted by the protocol which is pegged 1:1 to the staked asset.
The liquid staking token is burned when redeemed.
While receiving staking rewards, stakers can use the liquid staking tokens for crypto trading, yield farming, lending, etc. to earn extra rewards.
Many protocols charge a fee for liquid staking. For example, the largest liquid staking protocol Lido charges a 10% fee, which is split between Lido’s node operators and the Lido DAO.
Before staking, it is important to research whether the APR offered by the protocol is reflected before or after this fee is applied.
Advantages & Risks Of Liquid Staking
As with all things crypto, liquid staking (which can be be part of liquidity mining) offers some great advantages but also harbors certain risks which users need to be aware of. Let’s look at the most important ones.
Liquid Staking Advantages
Utilize liquidity: Stakers can use the liquidity of staked crypto assets while earning staking rewards.
No minimum amount required: Many liquid staking platforms allow users to stake any amount they want.
No “unbonding period”: Some PoS blockchains such as Polkadot have an “unbonding period” of several days to weeks if users want to unstake their assets. However, if users decide to stake via liquid staking platforms, they can withdraw their assets immediately.
Many platforms payout rewards in real-time: Stakers can get their staking rewards and reinvest immediately.
No prerequisites: Users do not need to set up and maintain staking infrastructure which helps them to save money and time.
Additional earnings: Compounded rewards can be earned across the protocol’s DeFi ecosystem using the derivative token, just like the staked crypto asset.
Liquid Staking Risks
Derivative token price risk: The price of a derivative token could de-peg from the staked token.
Loss of derivative token: If the user loses the derivative token, access to the deposited assets could also be lost. However, for larger protocols that have a good DeFi ecosystem, users can buy back the derivative token from decentralized exchanges.
Smart contract security: There could be bugs or malicious code in the liquid staking protocol’s smart contracts. For this reason, it is very important to check if the protocol you are using has released a recent third-party audit report.
Slashing risk: If the validators from the protocol do something malicious, they will get slashed by the network, leading the participants to lose a portion of the staked tokens. However, if the protocol has many validators, then this risk is reduced. What is more, some protocols have an insurance fund to compensate for this kind of loss.
Low adoption: If the proof-of-stake blockchain the liquid staking protocol is using fails to reach wide adoption, this could lead to a decrease in the value of its native cryptocurrency as well as the derivative token.
Liquid Staking Stats
To get a better understanding of current trends in the liquid staking space, let’s look at some recent data on major decentralized crypto applications (dApps) and blockchains.
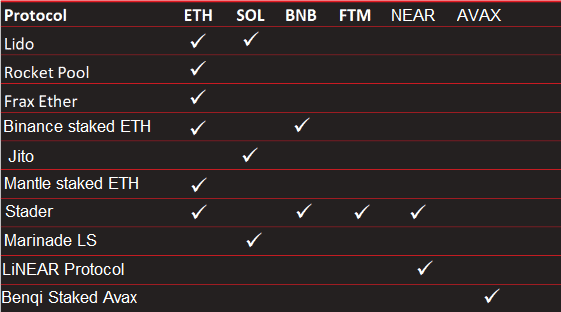
Overview: Top DeFi Liquid Staking Protocols And Supported Tokens
Here is a summary of supported tokens by top decentralized liquid staking platforms (data collected in April 2023):
The most supported cryptocurrency is Ether (ETH), followed by Solana (SOL), and BNB Smart Chain (BNB), . This is not surprising given that the Ethereum blockchain is at the forefront of DeFi. Let’s dig a little deeper into this.
📚 Read: 3 Ways to Stake Cardano (ADA)
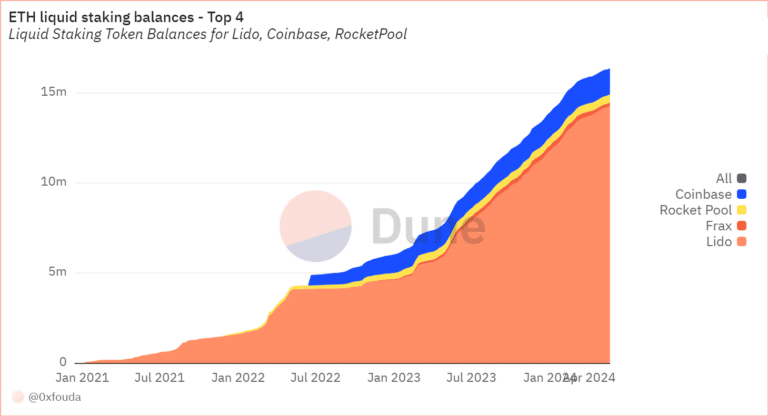
Comparison of Liquid Staking Protocols That Support ETH2
The following chart shows the ETH2 staking balance since January 2021.
We notice several things:
The number of ETH staked in various liquid staking protocols has increased steadily over the years – a development that appears to have been little affected by the last bear cycle.
Lido holds the lion’s share with over 80% of the staked ETH. Meanwhile, Coinbase was able to secure a large market share almost instantly. There is no sign of cannibalization.
The last point is particularly interesting considering the chart below.
The APRs (annual percentage rate – the investment interest users get for staking their crypto) of the various protocols show significant differences and vary between around 3.5% and almost 7%. However, a high APR does not necessarily mean that a protocol has a high balance. Lido could benefit from the first-mover advantage here.
📚 Read Next: Staking Pools: Lido vs Rocket Pool vs StakeWise
FAQs
What are the different staking solutions?
Earning staking rewards is a great source of passive income. There are several ways you can stake your crypto assets:
Self-staking: This means running your own node and becoming a validator while staking your cryptocurrencies. Normally, a minimum staking amount is required, for example, 32 Ether if you want to be a validator for the Ethereum network. At the moment, you need more than $62K in order to buy 32 Ether. Assuming you have the minimum required amount, there are two ways you can stake: an additional investment in the necessary hardware and some technical knowledge to set up a node. Alternatively, you can use paid services such as Allnodes to run your own hosted nodes. Self-staking is safe because you hold your own private keys.
Join a staking pool: If you do not have the minimum amount required and still want to stake and earn rewards, you can join a staking pool where multiple participants pool their tokens together to grant the pool operator validator status. In return, each token holder gets a share of the total rewards. A staking pool can be centralized, e.g. offered by a centralized crypto exchange such as Binance, or decentralized, e.g. offered by a decentralized finance protocol such as RocketPool.
Liquid staking: This is what we discussed in this article. Stakers can earn staking rewards while still utilizing the liquidity of their crypto assets.
What is a liquid staking APR?
A liquid staking APR (annualized percentage rate) is how much a staker will get as a staking reward for staking a fixed amount of chosen crypto asset with the liquid staking platform. From the staker’s point of view, it is called APY (annualized percentage yield). This rate is not fixed; it fluctuates every day.
Is liquid staking decentralized?
Liquid staking platforms can be centralized or decentralized, depending on the service provider. There are a number of decentralized liquid staking protocols such as Lido, Rocket Pool, Parallel Finance, and Ankr. There are also centralized exchanges offering liquid staking services such as Coinbase, and OKX. Here is an overview of liquid-staked ETH distribution.
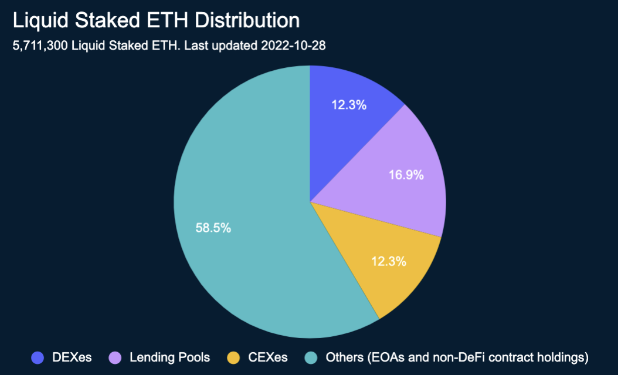
Source: nansen
Is liquid staking safe?
According to our research, most of the top protocols have security audit reports. This information can be found on the protocol’s page on DeFiLlama. It is also important to check if the protocol’s audit report is recent. Other ways to check the security of a protocol include CERTIK, DEFISAFETY, and CERTIFIED. Aside from reviewing security audit reports, it is crucial to verify whether the protocol has made its code open-source and provides a bug bounty program.

Siyu Ren Heinrich
5 years of experience in crypto research of writing practical blockchain and crypto analysis on Medium.
MSc in Computer Science, BSc in Smart Engineering, and BSc in Economics and Statistics.
Michael has been active in the crypto community since 2017. He holds certifications from Duke University in decentralized finance (DeFi) and blockchain technology.
🍒 tasty reads

What Is Ether.fi? Liquid Staking Reinvented

What Is Wrapped Ether? Complete wETH Guide

Impermanent Loss in DeFi: The Complete Guide

What is GMX? DeFi Perpetual Exchange 2024 Guide

What Is Defi Liquidity Mining and How Does It Work?