Staking Ether allows users to earn rewards by actively participating in and securing the Ethereum blockchain network.
Written by: Mike Martin | Updated July 26, 2024
Reviewed by: Ryan Grace
Fact checked by: Laurence Willows

Owning ether (ETH) without staking is like keeping money under a mattress – earn some passive income on your idle coins!
In this article, we’ll show you the 5 best ways to stake your Ethereum.
🍒 tasty takeaways
Ethereum has transitioned from proof-of-work (PoW) to proof-of-stake (PoS) through an upgrade called The Merge.
Stake your coins with a centralized exchange (CEX).
Delegate your ether to a protocol like Lido to stake on your behalf.
Stake as a service through Rocket Pool.
Buy a leveraged staking token from Index Coop.
If you have 32 ETH, you can run a staking node on Ethereum.
Summary
| Staking Method | Description | Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| Centralized Exchange | Stake crypto through exchanges like Coinbase or Binance. They handle staking on your behalf. | Purchase and hold ETH on the platform. |
| Staking Pool | Contribute crypto to a decentralized staking pool like Lido. | Hold ether in a self-custody wallet and delegate to a protocol. |
| Staking as a Service | Platforms like Rocket Pool allow users to run a node for their protocols. | At least 8 ETH to run a node on Rocket Pool. |
| Leveraged Staking Token | Buy a leveraged staking token from protocols like Index Coop. | Buy icETH token, a leveraged staking token. |
| Run a Staking Node | Run your own validator node on the Ethereum network for highest returns. | At least 32 ETH and technical knowledge on running a node. |
What is Ethereum Staking?
The Ethereum blockchain network switched its consensus layer from proof-of-work (PoW) to proof-of-stake (PoS) in an event dubbed The Merge to help its scalability issues.
PoW networks (like the Bitcoin network) rely upon ‘miners’ to validate transactions and continue the blockchain. PoS networks (Ethereum 2.0) rely upon ‘validators’ to do these tasks by ‘staking’ the coins native to their network. For the Ethereum network, this coin is ether, or ‘ETH’.
📚 Read: What is Crypto Staking And How Does it Work?
How Does Validation/Staking Work?
In validation, a blockchain network randomly chooses a computer to do the math required to verify transactions and add new blocks to the blockchain. In order to be in the selection process, you have to:
Own ether (ETH)
Stake your ether
Once your ether is staked, you’re in the pool of possible candidates to validate the next block.
So why would you want to validate?
Because you earn rewards! Customers have to pay fees (gas fees) to have their buy and sell orders, NFTs, and smart contracts added to a blockchain. Validators get to keep these network/transaction fees for their work!
Can Anybody Stake ETH?
Yes!
But in order to operate a full node with Ethereum, you need to stake at least 32 ether (ETH). That’s about $100,000 in 2024!
But you can still partake in staking activities without having a computer (validating rig) or this amount of ETH.
🏃♂️ Let’s find out how!

1. Stake Through a Centralized Exchange
One of the easiest ways to stake crypto is through a cryptocurrency exchange, like Coinbase, Kraken, Gemini, or Binance. You simply purchase ETH on their platform and they stake this crypto on your behalf.
Rewards on staking through a CEX are generally less attractive than those rewards offered in decentralized finance (DeFi).
Additionally, holding crypto on CEXs can be dangerous (remember what happened to FTX?)
On CEXs, you do not have direct access to your private keys. Therefore, you can’t be sure an exchange is holding your crypto 1×1 and not trading on it!
This is why most people advise holding crypto in a self-custody crypto wallet, where you have complete ownership over your digital assets.
There is an expression in crypto:
“Not Your Keys, Not Your Coins"
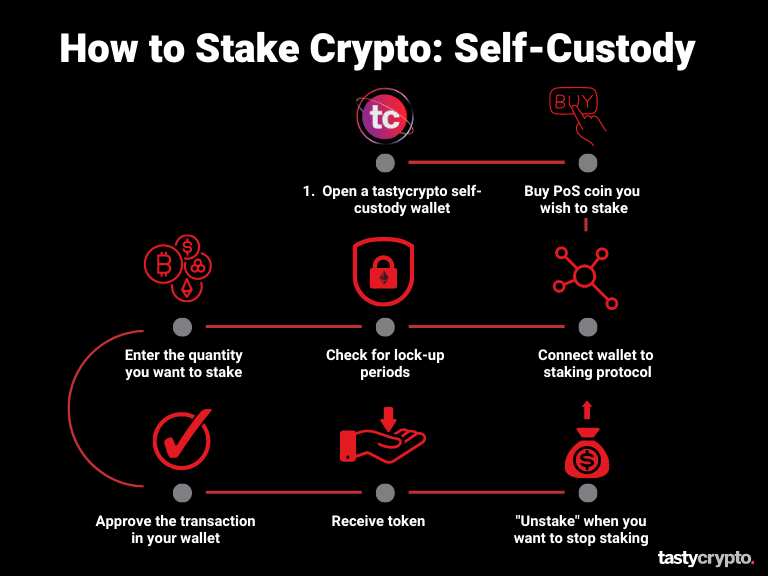
2. Join a Liquid Staking Pool
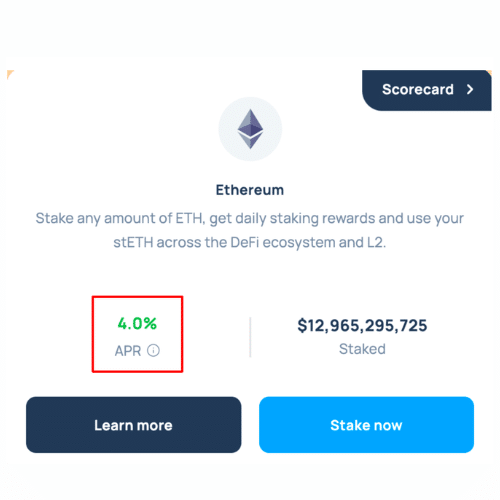
If you hold ether in a self-custody wallet, you can connect that wallet to a decentralized application (dApp) and delegate your crypto to that dApp to stake your ETH on your behalf.
You simply contribute crypto to their existing validating pools. No hardware is required for you.
Currently, Lido is the most popular crypto staking dApp in terms of total value locked (TVL).
Here’s how you stake with Lido:
Purchase ETH on a decentralized exchange like Uniswap
Connect a self-custody wallet (e.g. tastycrypto or Metamask) to the Lido website
Choose the cryptocurrency you want to stake (they also stake Polygon, Solana, and others!)
Enter the amount you want to stake
Confirm the transaction in your wallet
Receive your “staked ETH (stETH)” ERC20 token representing your share in the pool
Generally, you can ‘unstake’ your ETH whenever you want – the proceeds will represent your initial investment plus any staking rewards accrued.
The great thing about this option is that liquid staking protocols like Lido offer a liquid staked token (LST) in exchange for deposited ETH, which you can use in decentralized finance (DeFi) while your ETH is locked, thus maximizing potential profits.
📖 Read: Here’s how ‘liquid staking’ in crypto works
3. Staking as a service
Some staking platforms allow users to run a node for their protocols. This is helpful for people who still want to stake via a node, but don’t have the 32 ETH that the Ethereum network requires.
Rocket Pool, for example, allows users with only 8 ETH to run a node on their protocol.
Notice the higher APR that Rocket Pool pays when you stake + run a node.
Of course, there are risks to running a node – you could be penalized (lose your staked crypto) if your computer is down when the network calls on you to validate a block!
4. Buy A Leveraged Staking Token

There are some protocols out there like Index Coop that employ a leveraged liquid staking strategy. With this strategy, all you have to do is buy a token.
Let’s jump to the protocols’ website to see how this works!
“The icETH token is deployed to mainnet Ethereum. In execution, stETH is deposited to Aave to use as collateral to borrow ETH. This ETH is exchanged for additional stETH which is also deposited back into Aave to create the leveraged position.”
— Index Coop
At the moment, I would advise against this strategy. Why? Look at the APY.
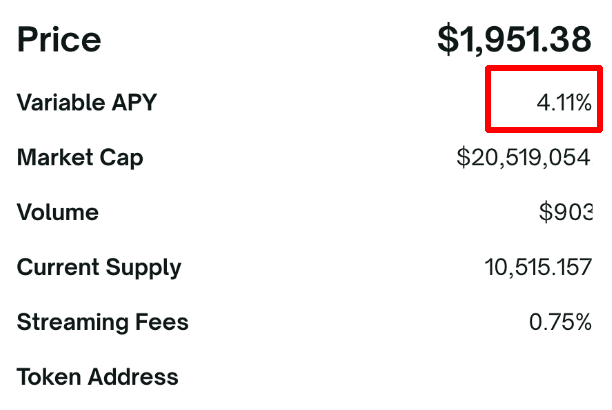
This is comparable to staking via a pool, which has much less risk.
Since Index Coop’s process involves an entire ecosystem of protocols, smart contract risk is high here. However, there are times when this yield is far greater than normal liquid staking pools APYs. Yield farming opportunities arise when this happens.
It’s all about your risk/return appetite.
📚 Read: 6 Ways to Leverage Your Crypto
5. Run a Staking Node
Our last option will garner you the highest returns for staking, but it also presents the most risks: running your own validator.
Staking directly with the Ethereum network does have its upsides. Here are a few:
Your data is private
No censorship
You are an active participant in the community and have a voice
High yields
However, as we learned with running a node by Rocket Pool, there are risks. If you have hardware issues, or your internet is down, you can be penalized heavily by the network (slashing).
To run an Ethereum node, you really need to know what you’re doing! And have at least 32 ETH at your disposal.
Related Articles:
FAQs
In order to stake directly for the Ethereum network, you need 32 ETH. However, you can stake any amount of ETH you want by delegating your crypto to a staking protocol like Lido, which in turn adds your crypto to a staking pool.
Yes, staking ETH is generally considered a low-risk way to make a profit.
Though staking crypto does come with risks (hardware risk and smart contract risk), the pros generally outweigh the cons.
It is possible to lose some or all of your ETH 2.0 if you choose to stake it. For example, if you are running a node and your node is down when you are called upon to stake, the Ethereum network will penalize you by taking away a portion of your staked ETH.
Yes, staking crypto is a taxable event and is generally subject to income tax. Koinly can be used to help do crypto taxes.
Yes – to become a validator on Ethereum, users must invest a minimum of 32 ETH. However, you can stake any amount of ETH you want by joining a staking pool like Lido.
In DeFi, the most popular protocols to stake ETH include Lido and Rocket Pool.
The beacon chain is a vital component of the Ethereum 2.0 upgrade that organizes consensus and manages the validators for the network.
‘Slashing’ occurs in ETH staking when a validator node breaks the rules. This can result in a loss of staked assets or even removal from the network.
Some blockchains require their validators to ‘lock up’ their staked coins for a set duration before they can be withdrawn. This helps to assure new blocks are always being added to the chain.
Additional Viewing:

Mike Martin
Mike Martin formerly served as the Head of Content for tastycrypto. Before joining tastycrypto, Michael worked in the active trader divisions of thinkorswim, TD Ameritrade, and Charles Schwab. He also served as a writer and editor for projectfinance.
Michael has been active in the crypto community since 2017. He holds certifications from Duke University in decentralized finance (DeFi) and blockchain technology.


The Core Blockchain and DeFi Ecosystem: What You Need to Know

7 Best DePIN Crypto Projects

What Is Symbiotic and How Does It Work in 2024?

Ethereum vs Ethereum ETFs – 5 Major Differences