Arbitrum, Optimism, and Polygon are layer 2 scaling solutions designed to overcome the limitations of the Ethereum blockchain. In this article, we explain the technical background and compare the strengths and weaknesses of these layer 2 networks.
Written by: Siyu Ren Heinrich & Anatol Antonovici | Updated June 24, 2024
Reviewed by: Mike Martin
Fact checked by: Ryan Grace
Arbitrum, Optimism, and Polygon are the most widely used general-purpose Ethereum layer 2s. Let’s now stack them side-by-side to determine the best one!
🍒 tasty takeaways
Different on-chain and off-chain solutions are being developed to scale the Ethereum blockchain.
Arbitrum and Optimism account for over 60% of the growing layer 2 sector.
Optimism is an optimistic roll-up that shares the security of the Ethereum mainnet but takes 7 days to finalize transactions.
Arbitrum comes in two forms – Arbitrum One, which is an optimistic roll-up, and Arbitrum Nova. The latter comes with lower fees but is less decentralized.
Polygon comes in two forms – Polygon POS, which benefits from fast transactions, and robust sidechain-technology. Polygon zkEVM is very secure but requires special hardware.
🚨 In June of 2023, Optimism completed its Bedrock upgrade. This hard fork created lower gas fees and faster block confirmations.
Summary
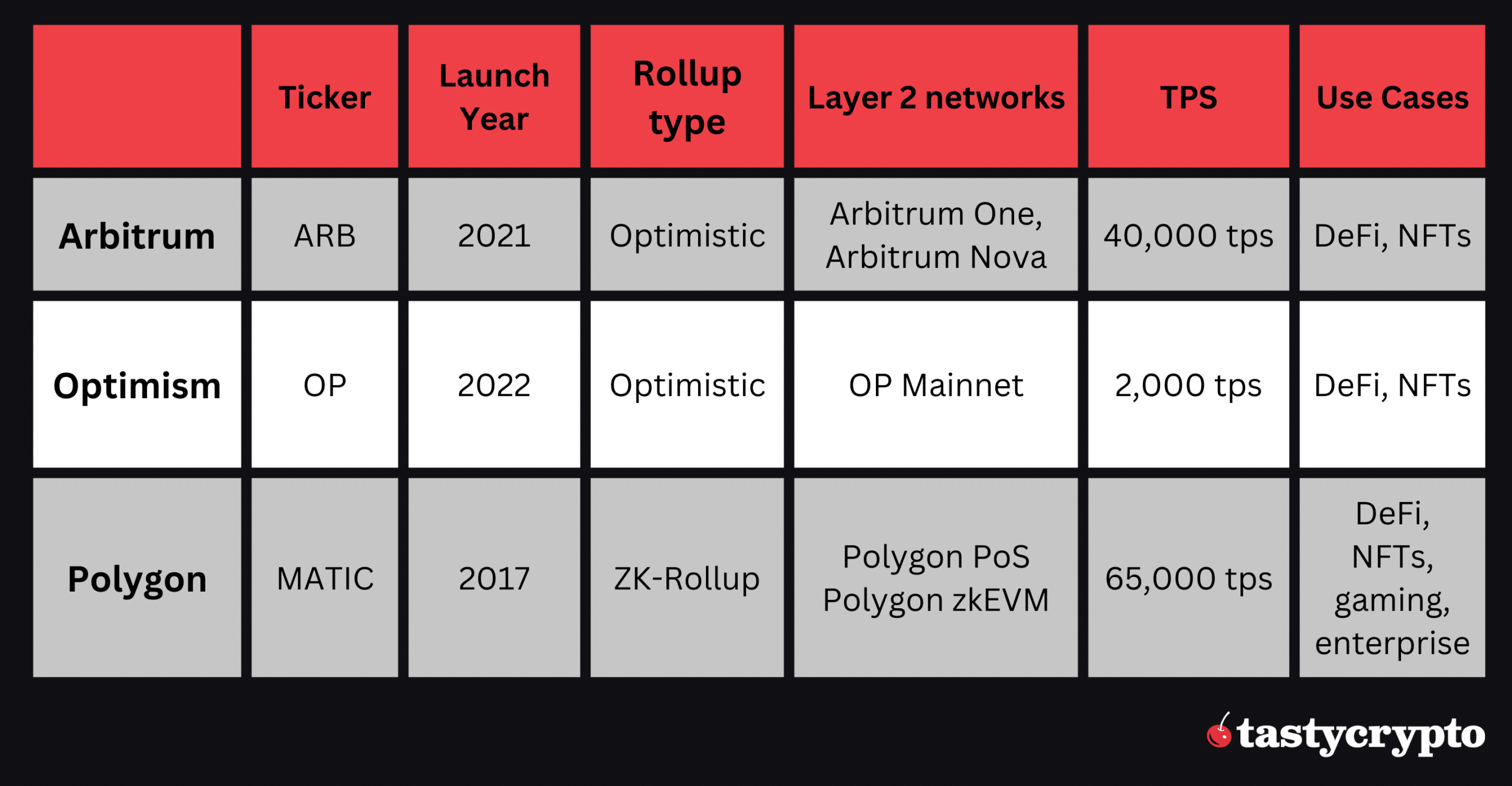
| Feature | Arbitrum | Optimism | Polygon |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mainnet | Ethereum | Ethereum | Ethereum |
| L2 Type | Optimistic Rollup | Optimistic Rollup | Sidechain, ZK Rollup |
| Token | ARB | OP | MATIC, POL |
| Use Case | Efficient Transactions | Compatible with EVM | High Volume Applications |
| Pros | Speed, Low Fees | EVM Compatibility | Functionality, ZK Security |
| Cons | Challenge Period | Limited Languages | Complexity for Users |
Arbitrum, Optimism & Polygon: Layer 2 Solutions for Ethereum
The Ethereum blockchain has successfully upgraded to adopt the Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus algorithm, but many decentralized applications (dapps) still prefer layer 2 solutions to achieve greater scalability and performance.
🍒 Layer 1 vs Layer 2: Blockchain Scalability Guide
Arbitrum, Optimism, and Polygon are Ethereum’s blockchain’s most popular layer 2 solutions, although Polygon has lost market share due to rise of the likes of Base, Blast, Linea, or zkSync Era. However, in terms of market cap, their native cryptocurrencis still account for almost 60% of the layer 2 sector, as tracked by Coinmarketcap
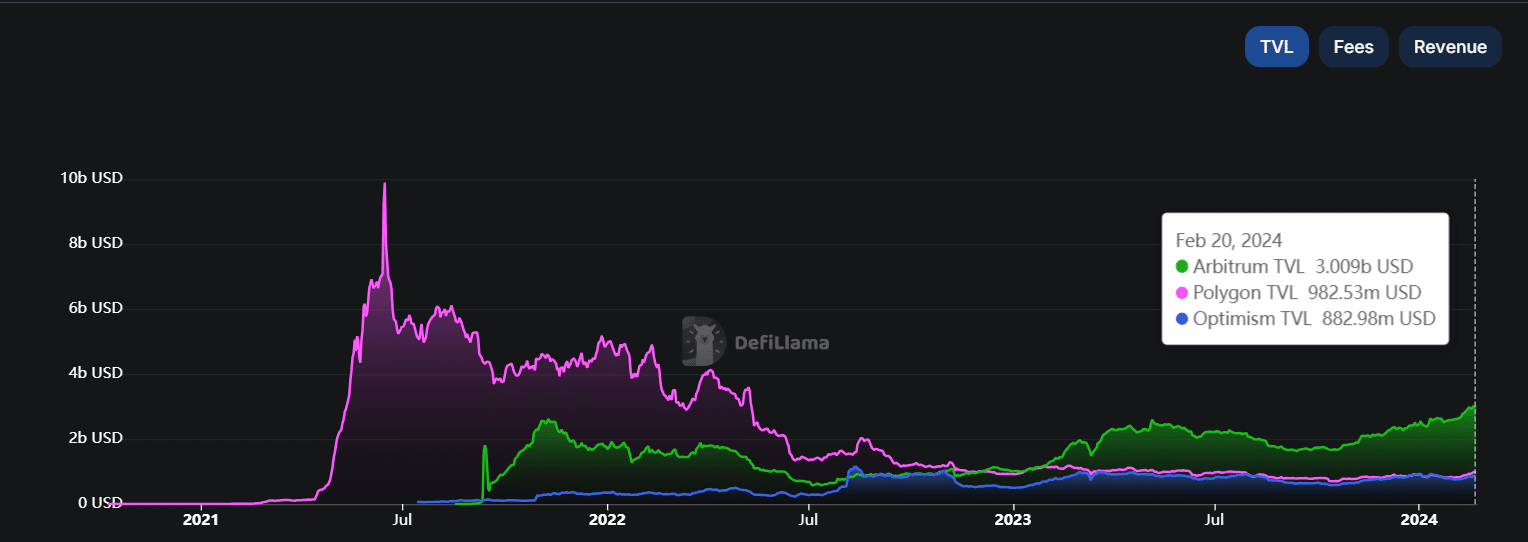
The three networks significantly impact decentralized finance (DeFi) by collectively holding approximately 4% of the total value locked (TVL) in the sector.
Source: DeFiLlama
Arbitrum and Polygon host over 500 DeFi protocols each, while Optimism is used by over 200 dapps.
All three layer 2s settle Ethereum transactions off-chain, but their methods differ. Here’s how 👇.
Arbitrum (ARB)
- Name: Arbitrum
- Token: ARB
- Mainnet: Ethereum
- L2 Type: Optimstic Rollup
How Does Arbitrum Work?
Arbitrum uses so-called optimistic rollups to merge transactions into batches and verify them outside of the Ethereum network.
🍒 7 Best Layer 2 Crypto Coins in 2024
They’re called optimistic because all transactions carried out on Arbitrum are treated as valid immediately. However, there is a challenge period to filter out bad transactions. Users are able to dispute any transaction by posting fraud proof up to seven days after execution.
This approach enables Arbitrum to achieve greater efficiency.
Arbitrum Ecosystem
Arbitrum offers two L2 chains:
- Arbitrum One is the Optimistic Rollup mainnet. It runs transactions on the Arbitrum Virtual Machine (AVM) extension, which is compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM).
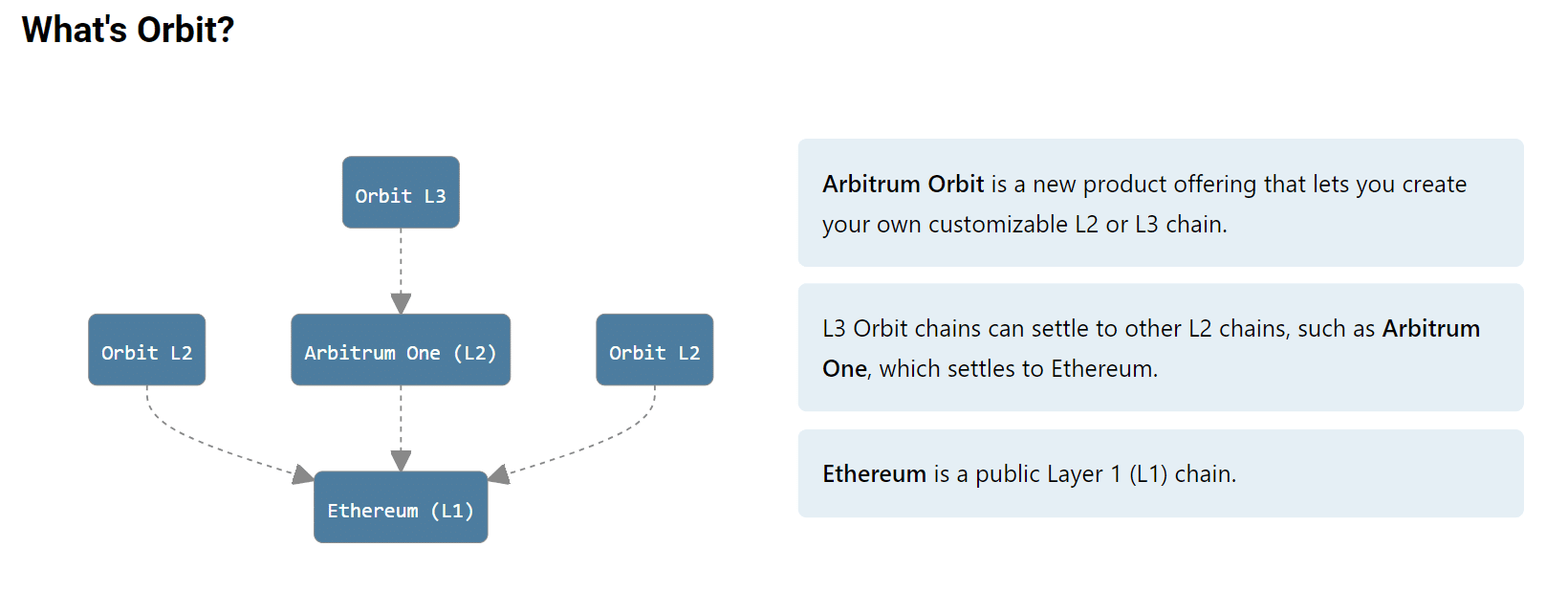
With the Nitro upgrade, this Optimistic Rollup chain improved its speed and reduced gas fees. - Arbitrum Nova is also built with Nitro and is specially developed for dapps like gaming, social, and non-fungible token (NFT) projects which come with high transaction volumes and demand very low transaction fees. This is achieved using the AnyTrust model, which is not an Optimistic Rollup protocol. In exchange for lower fees, its data availability is managed by a fixed permissioned set of entities called “Data Availability Committee (DAC).”
Developers can use Arbitrum Orbit to create customized Rollup or AnyTrust chains, being able to configure parameters like throughput, gas token, challenge period, and more.
Source: Arbitrum
The native ARB coin fuels the Arbitrum ecosystem.
Optimism (OP)
- Name: Optimism
- Token: OP
- Mainnet: Ethereum
- L2 Type: Optimstic Rollup
How Does Optimism Work?
Optimism, now known as the OP Mainnet, is a layer 2 scaling solution that uses technology similar to that of Arbitrum One. Its optimistic rollups also bundle Ethereum transactions to settle them outside the mainnet for greater efficiency.
Optimism introduced the Optimism Virtual Machine (OVM) extension to achieve compatibility with the EVM. However, while Arbitrum lets developers build in popular programming languages like Rust and C++, Optimism supports Ethereum’s Solidity.
OP Mainnet also has a 7-day challenge window for verifiers to check transactions, but it relies on single-round fraud proofs conducted on Ethereum compared to Arbitrum’s multi-round fraud proofs on its L2.
Optimism’s native token is OP, which uses the ERC-20 token standard.
Polygon (MATIC)
- Name: Polygon
- Token: MATIC, POL
- Mainnet: Ethereum
- L2 Type: Sidechain, ZK rollup
How Does Polygon Work?
Polygon, formerly known as Matic, represents a Layer 2 ecosystem that leverages multiple methods to streamline Ethereum transactions.
The Polygon network includes 2 Ethereum scaling solutions.
1. Polygon PoS
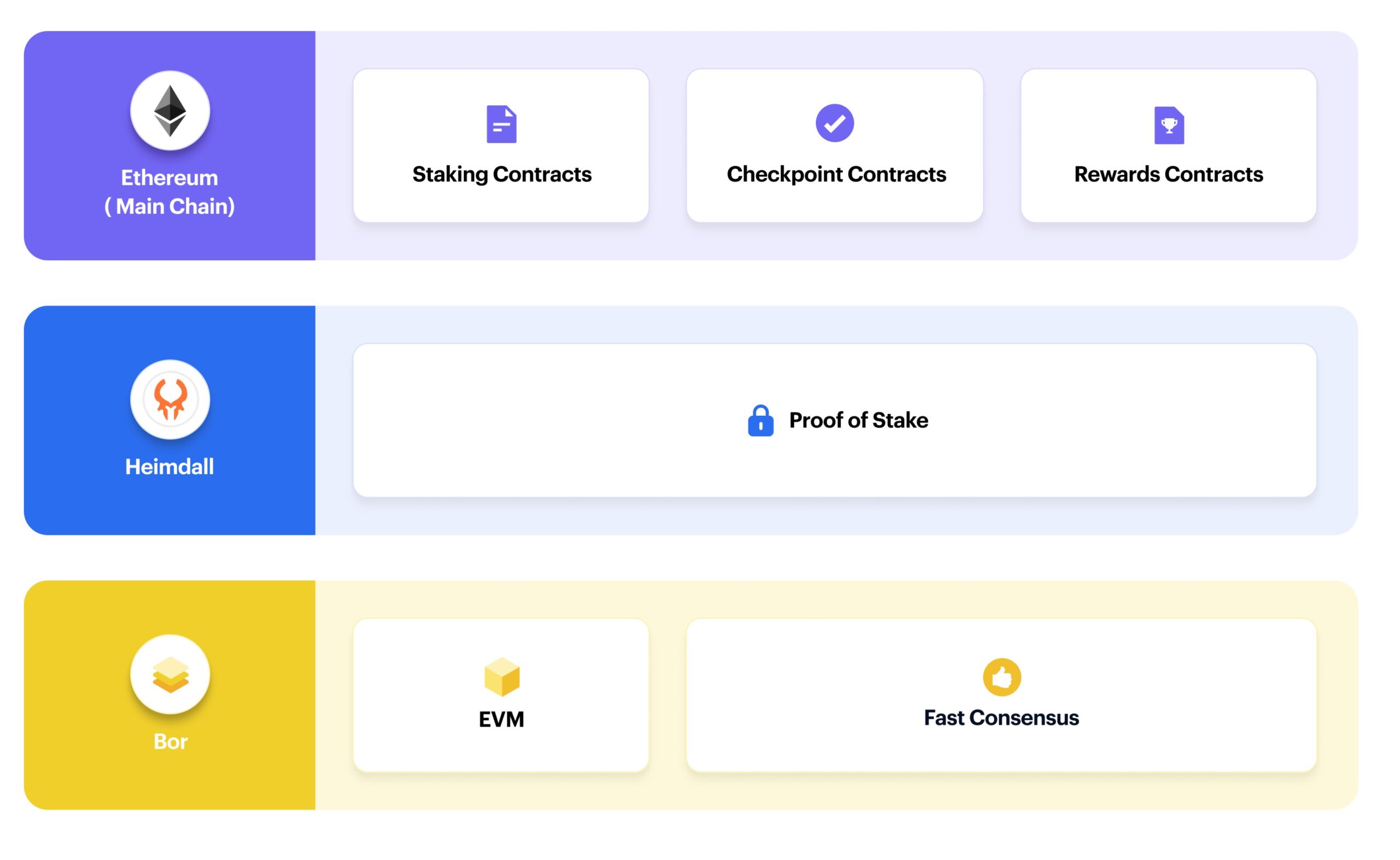
The first is Polygon PoS, an Ethereum sidechain that uses the PoS consensus. The network’s architecture comprises 3 layers:
- Ethereum layer: a group of smart contracts on the Ethereum main chain.
- Heimdall layer: a set of PoS Heimdall nodes running in parallel to the Ethereum mainnet.
- Bor layer: a set of block-producing Bor nodes shuffled by Heimdall nodes.
Source: docs.polygon
2. Polygon zkEVM
Polygon zkEVM is a layer 2 solution that uses zero-knowledge (zk) rollups.
Like Optimistic rollups, ZK rollups bundle Ethereum transactions into batches to settle them off-chain. However, they use a complex cryptography mechanism – ZK proof – to prove transaction validity without accessing too many details. This way, ZK rollups don’t need any challenge window, reaching finality much faster while keeping transaction details private.
Unlike the sidechain, Polygon zkEVM shares the security and decentralization of Ethereum.
Polygon is also developing Polygon Miden, a ZK rollup network running on the Miden VM – a virtual machine that focuses on ZK-friendliness over EVM compatibility.
Polygon Tokens
Polygon’s MATIC is an ERC-20 token that retains the original name of the project. It is used for governance, staking, and paying gas fees.
To finalize the rebranding effort, MATIC is being incrementally converted to POL (Polygon Ecosystem Token) at a 1:1 ratio, a process expected to be completed within 4 years.
As of today, MATIC is the 14th-largest cryptocurrency, with a market cap of $9.4 billion. POL started trading in November 2023 and has a similar price. Its valuation has recently exceeded the $100 million mark.
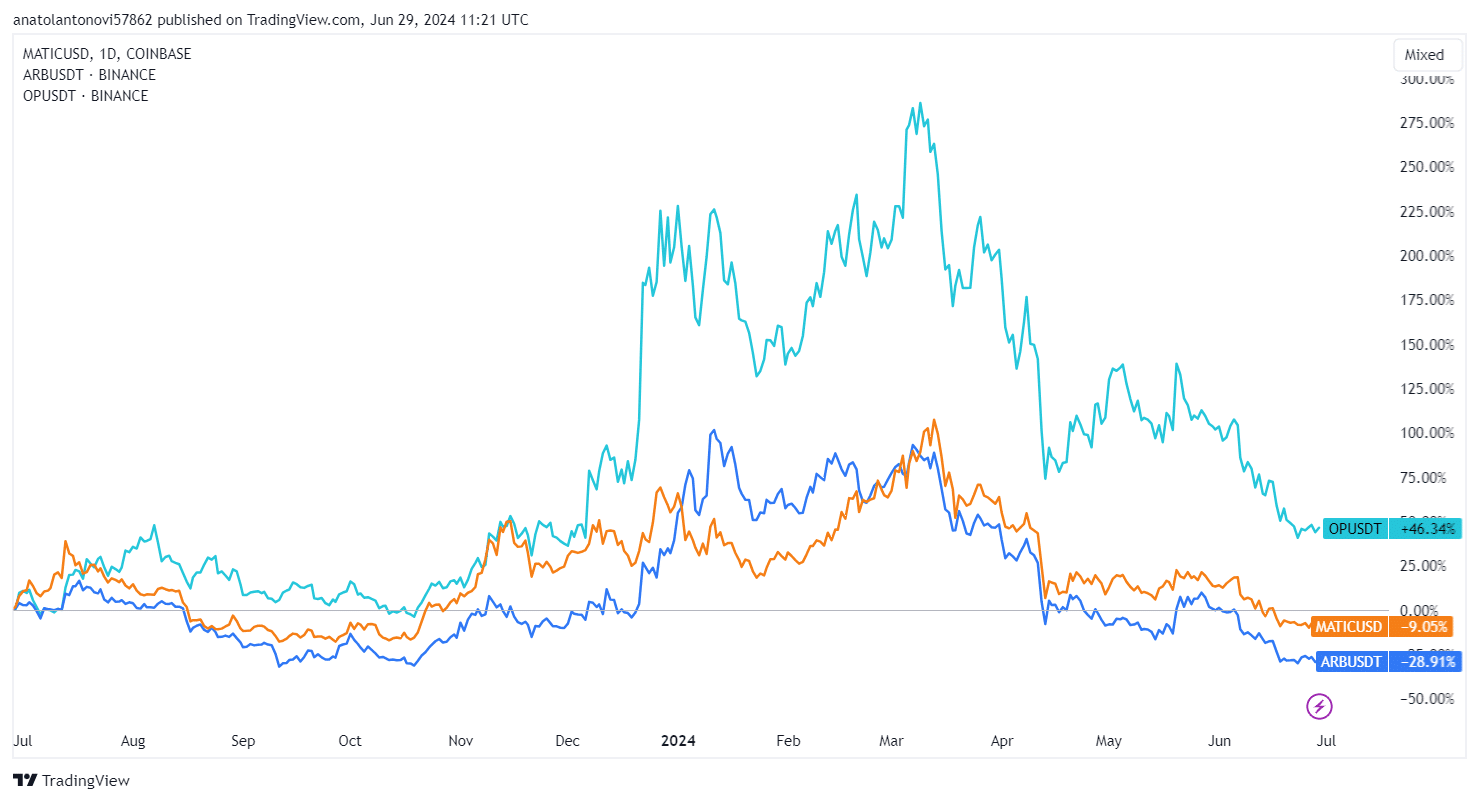
Arbitrum vs Optimism vs Polygon: Price History
The below chart compares the 1 year price history of ARB, OP and MATIC (POL).
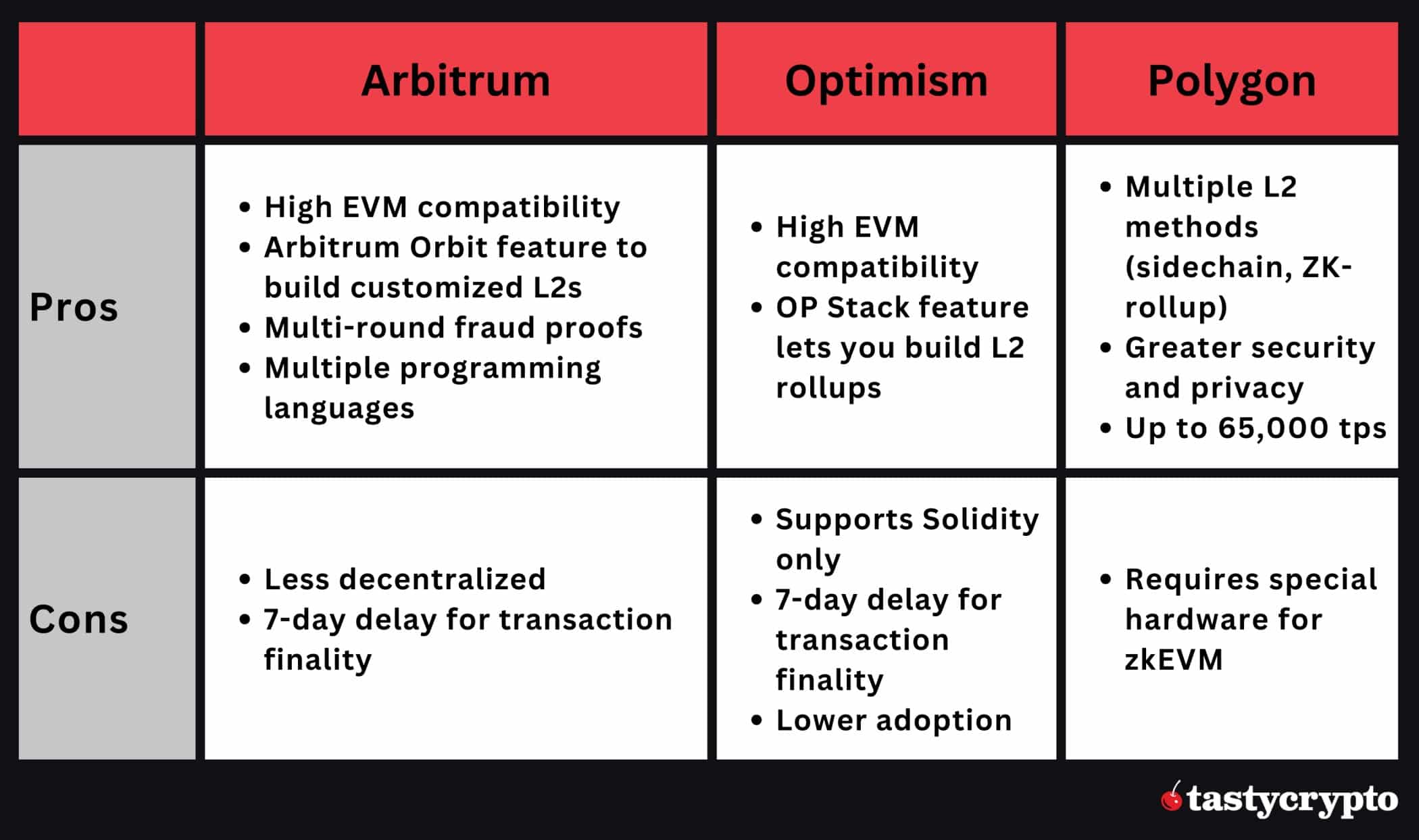
Arbitrum vs Optimism vs Polygon: Which Is Best?
It’s difficult to conclude which layer 2 is best as each protocol has its pros and cons. Much depends on the nature of the project and the needs of its users.
As it stands, Arbitrum is the most popular Optimistic rollup solution, while Polygon is used for its ZK rollup network and greater functionality.
Arbitrum has the largest share across DeFi, while Polygon is preferred by NFT projects.
Here are the pros and cons of each protocol:
FAQs
Arbitrum, Optimism, and Polygon are layer 2 scaling solutions for Ethereum. They offer faster and cheaper ways to execute Ethereum transactions.
Both Arbitrum and Optimism use Optimistic rollups, which group Ethereum transactions into batches while considering them valid unless challenged within a 1-week period. Polygon operates a sidechain and a ZK rollup network, which also settles Ethereum transactions off-chain but uses ZK proof to validate transactions right away.
It depends on the specific needs. Arbitrum is the best Optimistic rollup, while Polygon offers one of the best ZK rollup solutions. Optimistic rollups are favored for their speed and transparency, while ZK rollups provide greater security and privacy.
ARB, MATIC, and OP tokens are listed on most crypto exchanges, including decentralized exchanges (DEXs) like Uniswap. You can also buy these tokens inside the tastycrypto app using the swap feature.
🍒 tasty reads


The Core Blockchain and DeFi Ecosystem: What You Need to Know

7 Best DePIN Crypto Projects

What Is Symbiotic and How Does It Work in 2024?

Ethereum vs Ethereum ETFs – 5 Major Differences


Anatol Antonovici
6+ years of experience writing for crypto brands and blockchain firms, including Coindesk, Cointelegraph, Bitcoinist, CryptoPotato, Algorand, and OTCTrade.com

Siyu Ren Heinrich
5 years of experience in crypto research of writing practical blockchain and crypto analysis on Medium.
MSc in Computer Science, BSc in Smart Engineering, and BSc in Economics and Statistics.
Michael has been active in the crypto community since 2017. He holds certifications from Duke University in decentralized finance (DeFi) and blockchain technology.