Definition: A blockchain bridge is a Web3 protocol that allows users to send digital assets from one blockchain to another.
Written by: Siyu Ren Heinrich | Updated July 5, 2024
Reviewed by: Mike Martin
Fact checked by: Ryan Grace

Each blockchain forms its own closed ecosystem. This poses a problem whenever users want to transfer assets from one network to another. For example, users cannot simply move their Bitcoin to the Ethereum blockchain.
Blockchain bridges solve this problem as they enable seamless interaction between different networks. In this article, we explain everything you need to know about bridges in blockchain technology.
🍒 tasty takeaways
- Blockchains are isolated ecosystems; bridges address this by facilitating cross-chain transactions.
- Blockchain bridges act as intermediaries, enabling smooth asset transfers between different blockchains.
- Crypto bridges are used for transferring assets between different blockchains. They are roughly divided into trusted (centralized) and trustless (decentralized).
- There are two primary types of bridges: Trusted (centralized) and Trustless (decentralized).
- Using exchanges for cross-chain transfers can be costly and time-consuming; bridges streamline this process.
- Bridges are among the largest and most important DeFi protocols, some of which manage assets worth hundreds of millions of USD.
- This is risky because users have to trust centralized bridges with their assets, while trustless protocols are often targeted by hackers.
Bridges Summary
| Category | Description |
|---|---|
| What are Blockchain Bridges? | Protocols that connect different blockchains allowing assets transfers. |
| Why Used? | To facilitate interoperability and overcome isolated blockchain ecosystems. |
| Types | Trusted/Centralized, Trustless/Decentralized, Unidirectional, Bidirectional. |
| Top 5 by Volume | Stargate, Arbitrum Bridge, Multichain, Polygon Pos Bridge, Optimism Gateway. |
| Risks | Centralized: Custodial and censorship risks. Decentralized: Vulnerabilities due to underlying code. |
| Security Measures | Regular audits, user due diligence. |
| Transaction Fees | Range from 0.05% to 0.3% depending on various factors. |
What Are Blockchain Bridges And Why Are They Being Used?
A blockchain bridge, also known as a crypto bridge or cross-chain bridge, is a protocol that connects two different blockchains. It enables users to transfer cryptocurrency from one chain to another.
You can also transfer assets to another blockchain using a crypto exchange, such as selling bitcoin (BTC) for ether (ETH). However, depending on the platform, this can be quite time-consuming and costly in terms of fees, especially if you need to do it frequently. Blockchain bridges simplify this process.
Blockchain Bridge Use Cases
Blockchain bridges have several use cases that revolve around the interoperability of different blockchain networks. Here are a few examples:
Asset transfer between multiple blockchains: This is particularly useful when users want to move their funds to blockchains that offer unique features and access to certain decentralized applications (dApps).
Cross-chain DeFi: Crypto bridges allow users to leverage the benefits of multiple decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystems without being limited to a single blockchain.
More liquidity: By connecting different blockchain networks, bridges increase overall liquidity. Users can provide liquidity to liquidity pools on different blockchains.
Blockchain scaling and performance: Bridges can help with solving scalability problems by offloading transaction volume to other networks.
NFTs: Some bridges support the transfer of Non-fungible Tokens (NFTs) between different networks. This allows owners to access different marketplaces and applications.
What Types of Blockchain Bridges Are There?
There are four main types of blockchain bridges:
Trusted / Centralized Bridges
Trusted crypto bridges are run by people or organizations. A well-known example is Binance Bridge.
Because they rely on centralized services, users need to trust them.
An advantage of centralized bridges is that they are faster and cheaper than many trustless bridges.
Trustless / Decentralized Bridges
Decentralization is an essential part of DeFi. Thus, trustless bridges do not rely on a single authority but on smart contracts for handling all operations.
Users are responsible for their funds.
The bridge’s security depends on the security of the underlying blockchain and on the quality of the deployed smart contracts.
Generally, trustless crypto bridges have higher transfer fees than their centralized counterparts.
Unidirectional And Bidirectional Bridges
A unidirectional bridge lets you send funds only to the target blockchain but not back to the native blockchain.
A bidirectional blockchain bridge lets you freely trade assets between two blockchains.
Crypto Bridge Transaction Fees
Bridge fees are paid for every transfer. For most providers, bridge fees range from 0.05% to 0.3%. The actual costs depend on different factors such as whether the service is centralized or decentralized and on the blockchains involved. Transaction fees are usually paid in the same token that is transferred.
Some providers offer lower fees in return for staking their tokens.
What Are The Top 10 Crypto Bridges?
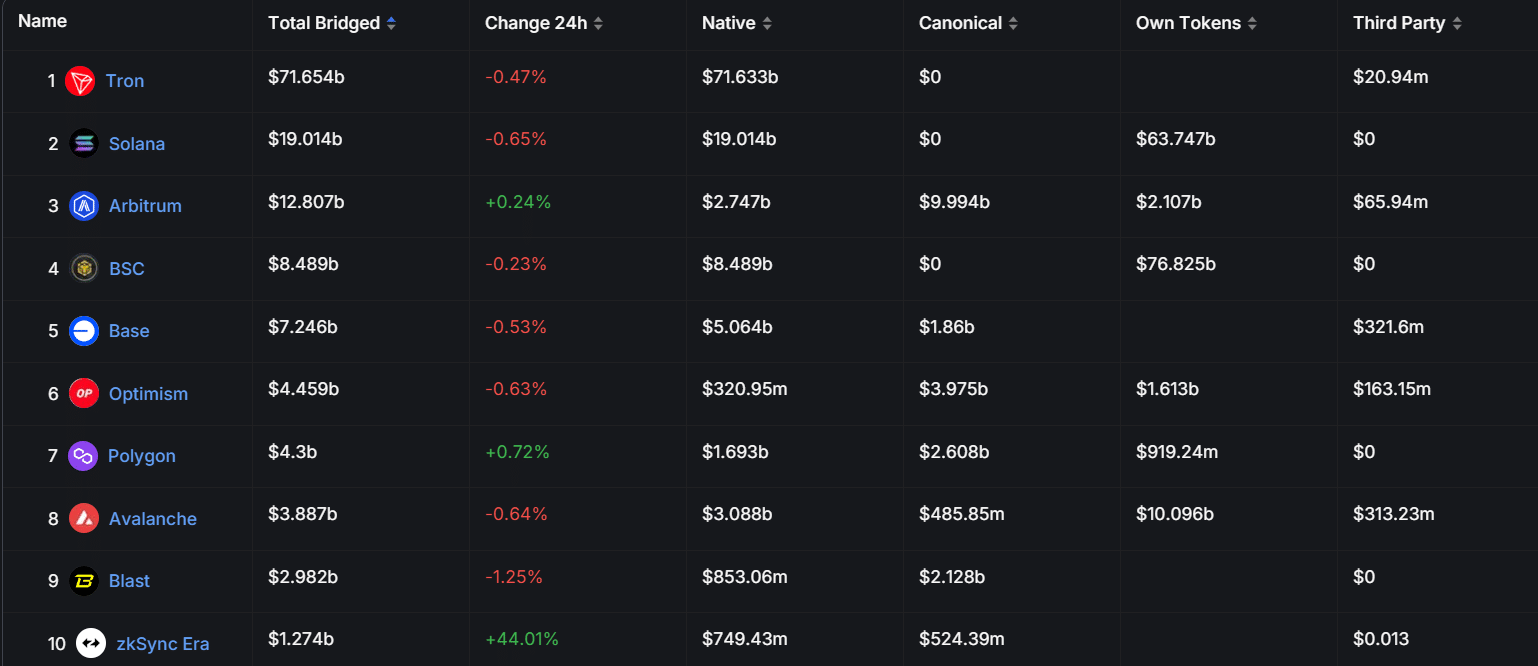
Here are the top 10 blockchains by the total value locked (TVL) in their bridges, as per DefiLlama:
Source: DefiLlama
Tron tops the list with $71.6 billion, followed by Solana ($19 billion), Arbitrum ($12.8 billion), BNB Smart Chain ($8.5 billion), and Base ($7.2 billion).
🍒 Arbitrum vs Avalanche vs Optimism: Which Is Best in 2023?
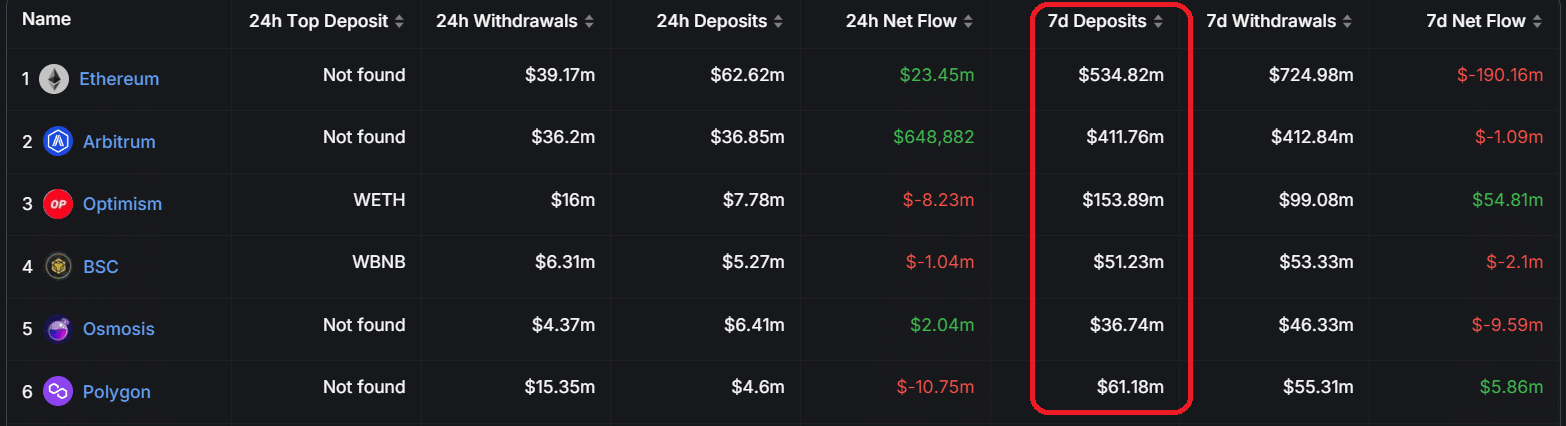
Next, let’s look at 7-day bridge inflows in USD by chain:
Source: DefiLlama
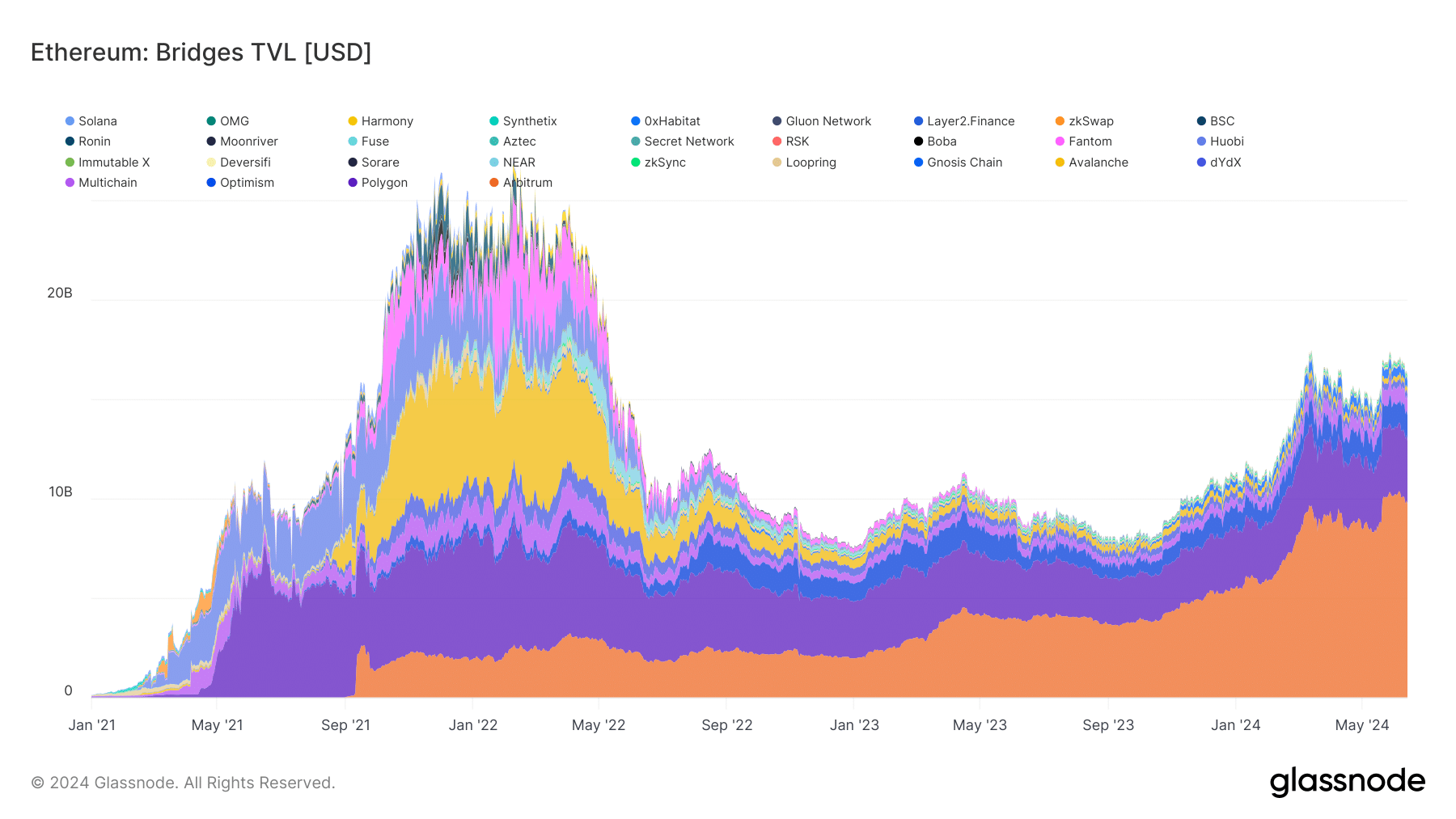
Today, Arbitrum is the largest bridge that connects to the Ethereum ecosystem, with over $10 billion in TVL, according to Glassnode. In June 2024, its dominance level reached a record 61%.
Source: Grassnode
Blockchain Bridge Security – What Are The Risks?
Since users need to lock their assets into smart contracts as part of their usage, the individual protocols hold enormous amounts of value. This makes them a preferred target for attacks.
Unfortunately, many protocols have vulnerabilities that can be used for crypto bridge exploits and hacks.
As centralized services, trusted bridges entail custodial and censorship risks for users. Custodial risk means that the operators of the bridge could steal the users’ funds. Censorship risk means that operators can stop the transfer of funds.
Decentralized crypto bridges also have vulnerabilities due to their underlying code and algorithms. Faulty smart contracts and other technology risks are among the main reasons for stolen crypto funds in recent years.
According to Chainalysis, cross-chain bridge hacks accounted for almost 70% of all stolen funds in 2022.
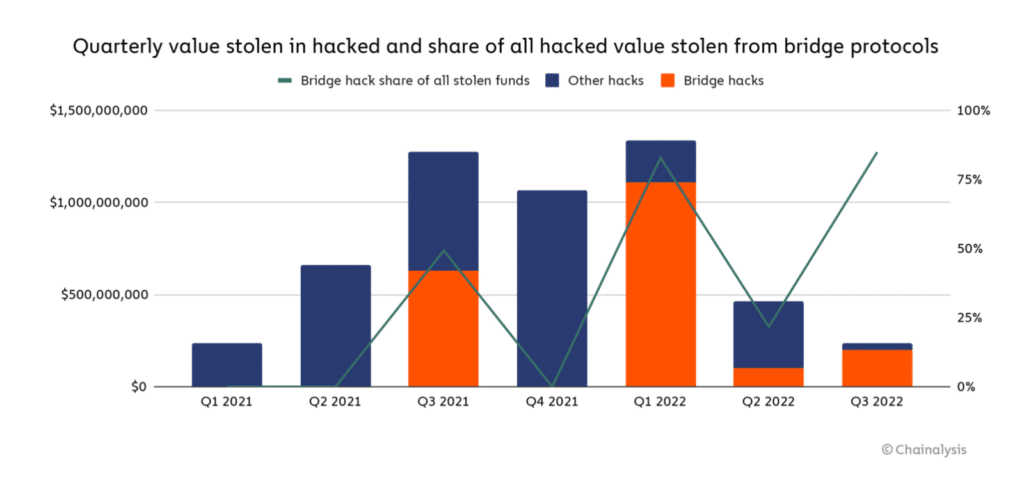
So far, no definitive solutions to these problems have been found. However, trustless bridges can minimize the risk of exploits and hacks by regularly conducting thorough internal and external audits of their codes and smart contracts. Accordingly, it is also important for users to subject bridges to a thorough due diligence process before using them in order to get as comprehensive a picture as possible of the security standards and possible risks.
FAQs
While a crypto bridge enables the transfer of crypto assets between different blockchains, crypto swaps refer to the exchange of digital assets within the same blockchain ecosystem – for example exchanging different ERC-20 tokens. Crypto bridges focus on cross-chain interoperability, whereas crypto swaps are centered around trading and exchanging digital assets.
The best blockchain bridge depends on the individual needs of a user. But in general, users want bridges that are secure and cheap. Some of the most frequently used bridges include Multichain, Allbridge, Stargate, and Polygon PoS Bridge.
The number of blockchains supported by a bridge depends on the respective provider. For example, Multichain currently supports over 90, CBridge 45, Anyswap 35, and Stargate 8 different blockchains.

Siyu Ren Heinrich
5 years of experience in crypto research of writing practical blockchain and crypto analysis on Medium.
MSc in Computer Science, BSc in Smart Engineering, and BSc in Economics and Statistics.
Michael has been active in the crypto community since 2017. He holds certifications from Duke University in decentralized finance (DeFi) and blockchain technology.
🍒 tasty reads

What Is Ether.fi? Liquid Staking Reinvented

What Is Wrapped Ether? Complete wETH Guide

Impermanent Loss in DeFi: The Complete Guide

What is GMX? DeFi Perpetual Exchange 2024 Guide

What Is Defi Liquidity Mining and How Does It Work?