Flash Loan Definition: A flash loan is a digital loan of cryptocurrency that is issued and repaid in a single transaction.
Written by: Anatol Antonovici | Updated August 26, 2024
Fact checked by: Ryan Grace

Imagine if it were possible to borrow money in seconds without collateral and be able to use it to generate profits. If you fail to make a profit, you simply reverse the borrowing transaction as if nothing happened. If you succeed, you repay the funds and remain with the profit.
This is exactly how flash loans work in decentralized finance (DeFi) – a major trend that leverages blockchain technology to build financial services.
Table of Contents
🍒 tasty takeaways
Flash loans are uncollateralized loans in decentralized finance (DeFi) that must be repaid within a single blockchain transaction, mainly using Ethereum’s smart contracts.
These loans don’t require collateral or income proof. If not repaid within the same transaction, the smart contract automatically reverses the loan.
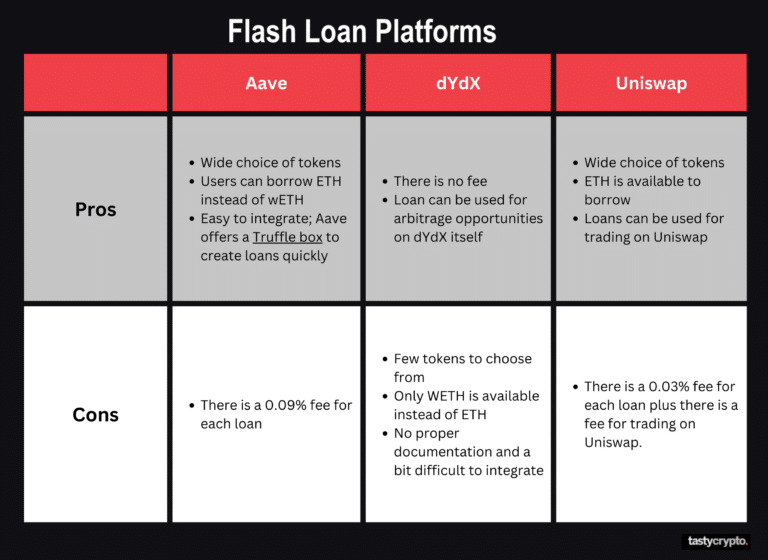
Aave made flash loans popular in 2020, but Marble introduced them in 2018. Platforms like Aave, dYdX, and Uniswap offer them.
Borrowers specify loan details in a smart contract. They receive funds, use them (e.g., for trades), and repay within the same transaction, often with a fee.
Flash loans are used for arbitrage, collateral swaps, and debt refinancing.
| Summary | |
|---|---|
| What Are Flash Loans? | Uncollateralized crypto loans repaid in a single transaction. |
| How Do Flash Loans Work? | Use smart contracts for instant borrowing and repayment. |
| Flash Loan Use Cases | Applications in arbitrage, collateral swaps, and debt refinancing. |
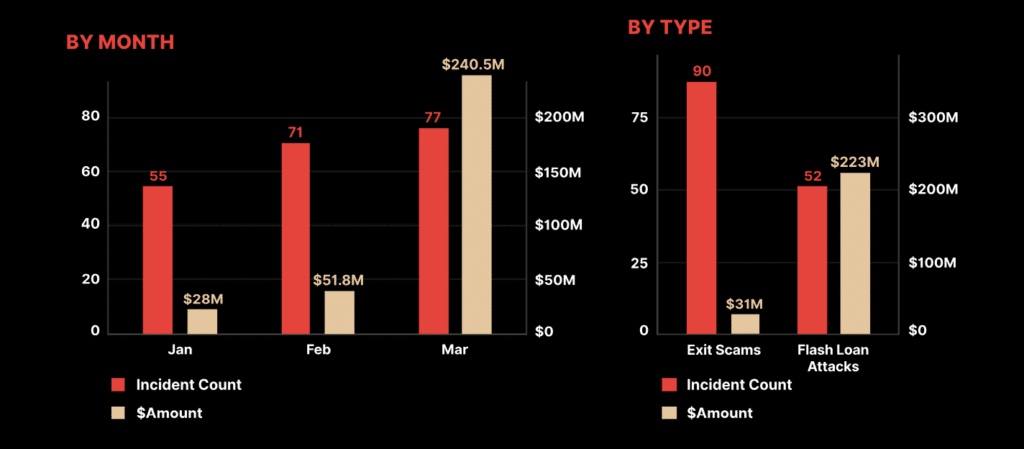
| Flash Loan Safety | Risks of flash loan attacks and security measures. |