Fees on centralized and decentralzied exchanges can vary widely. In this article, we’ll compare the top DEX and CEX trading fees.
Written by: Siyu Ren Heinrich | Updated June 14, 2024
Reviewed by: Mike Martin
Fact checked by: Ryan Grace

When choosing a cryptocurrency exchange, investors have a lot of things to consider. Security, liquidity, ease of use, and fees are all important criteria.
In this article, we are going to focus on the latter: fees.
High platform fees will inevitably lead to lower profit margins. A widely held belief is that decentralized exchanges (DEXs) offer lower transaction costs than centralized exchanges (CEXs).
In the sections that follow, we will compare the fees of the most popular crypto exchanges to determine whether or not this is indeed true.
Lowest fees for CEXs: Bybit, tastytrade, Currency.com, and Liquid.
Lowest fees for DEXs: Curve, Balancer, and Canto Dex.
🍒 tasty takeaways
Crypto exchanges charge fees for various processes. A basic distinction is made between fees for trading, deposits & withdrawals, and other processes such as loans and liquidations.
Trading costs also can differ depending on whether users act as a so-called maker or taker with makers usually being charged lower fees.
On average, maker fees are lowest on CEXs. On the other hand, the average taker fees on DEXs are the lowest.
In an individual comparison, some DEXs with 0% fees for makers and takers are the cheapest option.
What Is A Centralized Crypto Exchange (CEX)?
A centralized exchange, or CEX, is run by a company or a group of people. A CEX acts as a third party between crypto buyers and sellers. They also act as both brokers and custodians for crypto participants. Well-known CEXs include Binance, Kraken, and Coinbase.
Similar to traditional stock exchanges, CEXs are commonly regulated by relevant government authorities. CEXs must fulfill a set of legal criteria and obtain licenses to operate and offer services.
Because of this, when users want to open an account with a CEX, they need to go through a series of cumbersome KYC (Know Your Customer) and AML (anti-money laundering) verification procedures.
CEXs are preferred over DEXs by some crypto participants for the following reasons:
CEXs normally have very user-friendly interfaces and offer customer support services.
CEXs require little technical know-how.
CEXs offer a range of trading options and frequently offer leverage.
Because DEXs lack the function of exchange between fiat and cryptocurrencies, CEXs act as a source of DEX funding and withdrawal.
If a user forgets the password or account ID to a CEX, that user can retrieve the funds in the account because CEXs hold the private keys.
📚 Read: Crypto vs DeFi – How Do They Differ?
What Is A Decentralized Crypto Exchange (DEX)?
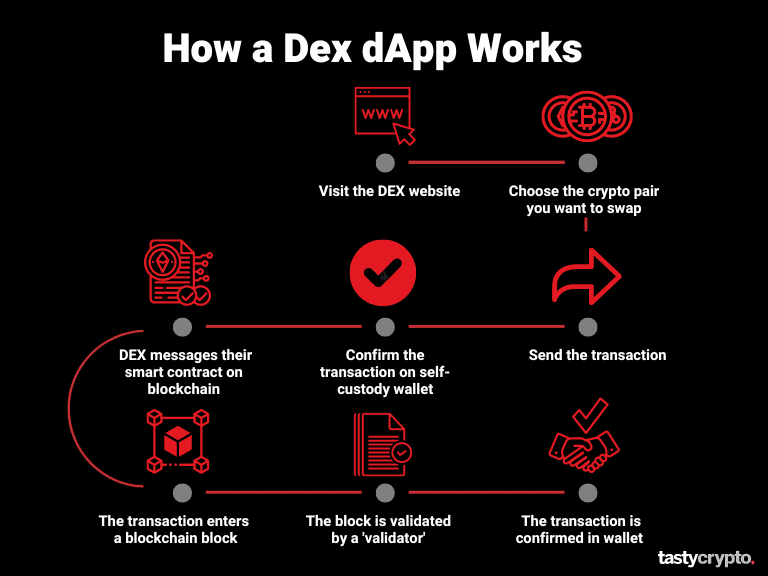
Decentralized exchanges are DeFi (decentralized finance) applications. They are built on blockchains that support smart contracts.
For example, the largest DEX by trading volume – Uniswap – was first built on the Ethereum network.
A DEX allows crypto traders to swap coins and tokens without a middleman. This makes transactions faster and cheaper. DEXs achieve this by bypassing intermediaries, which also typically claim a portion of the fees.
If you want to know more about DEXs, AMMs (automated market maker), liquidity pools, and impermanent loss, we recommend you check out our in-depth guide on decentralized crypto exchanges.
We will next look at three fees that apply to both DEXs and CEXs. Bear in mind that when using a DEX, most networks charge gas fees in order to validate and add transactions to the immutable blockchain.
3 Types Of Crypto Fees
There are three main types of fees that crypto exchanges charge.
1. Trading Fees
These are the ‘classic’ fees you pay to crypto exchanges to both swap crypto and convert crypto to cash (CEXs). These fees are usually higher on CEXs than DEXs.
🚨 If you’re trading crypto on a centralized exchange, you don’t pay gas fees – you pay maker/taker fees. Read how these fees work here!
2. Deposit & Withdrawal Fees
These fees apply when you transfer funds to or withdraw funds from your exchange wallet. Usually, CEX platforms also charge fees if you want to transfer fiat to your bank account – the so-called ‘cash out fee’.
3. Fees For Loans & Liquidations
In addition, many crypto exchanges offer other functions you need to pay for. For example, there are fees for borrowing funds. Another example is liquidation fees when your collateral needs to be liquidated. These can apply to both DEXs and CEXs.
🍒 tastytrade caps its crypto fees at 1% of purchase/sale price or $10 per order – whichever is less!
Now let’s take a look at the data!
Cryptocurrency Exchange Trading Fees Comparison
We used data from Coinmarketfees and from the websites of individual exchanges for the following analysis and to create the visualizations.
The data set includes a total of 62 DEXs and CEXs. Please note that for this comparison we referred to the base costs incurred for trades.
Distribution Of Maker & Taker Trading Fees
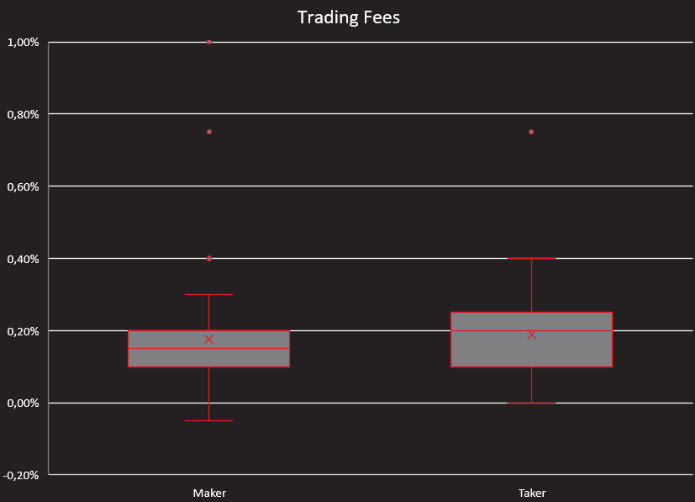
Trading costs can differ depending on whether you act as a so-called maker or taker.
Makers create a market for other traders and bring liquidity to an exchange. To incentivize market makers, exchanges usually have to pay a little bit less than takers who remove liquidity by filling available orders.
The below chart shows this.
📚 Read: Maker vs Taker Fees in Crypto
Makers
Trading costs for makers when using the examined platforms range from -0.05% to 1%.
First quartile: 0.1%
Median: 0.15%
Third quartile: 0.2%
Takers
Trading costs for takers when using the examined platforms range from 0.0% to 0.75%.
First quartile: 0.1%
Median: 0.2%
Third quartile: 0.25%
Now let’s look at these fees for both CEXs and DEXs.
CEX Vs. DEX – Which Has Lower Fees?
Many crypto investors believe that it is cheaper to trade on decentralized exchanges. But based on the data we used, calculating the average costs for makers and takers says something else:
Average CEX trading fees (maker): 0.174%
Average CEX trading fees (taker): 0.189%
Average DEX trading fees (maker): 0.185%
Average DEX trading fees (taker): 0.187%
Let’s see that in detail.
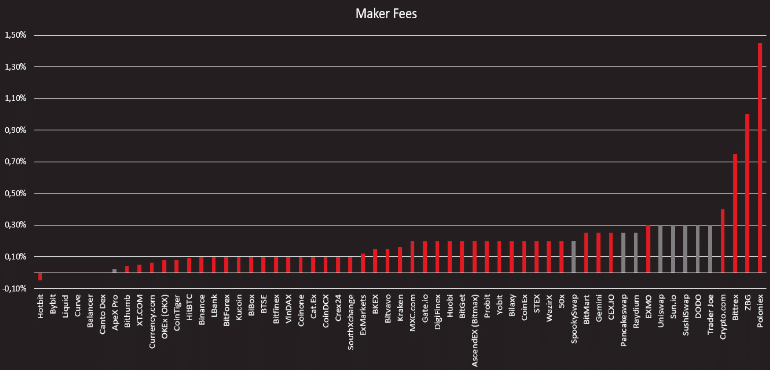
The chart below shows the CEX (red) and DEX (grey) trading costs for market makers.
And this chart shows the CEX (red) and DEX (grey) trading fees for market takers.
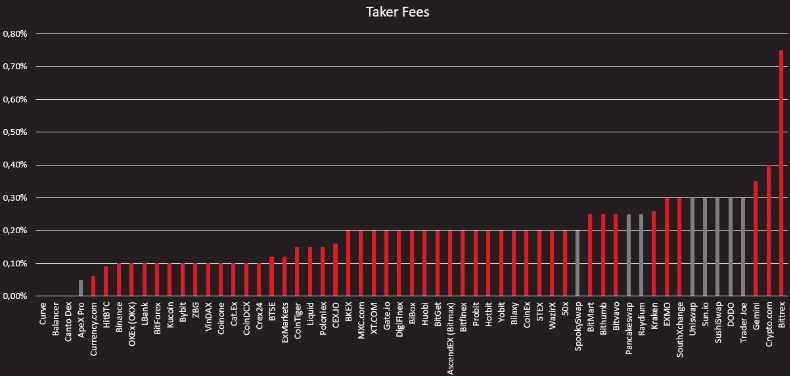
As these charts show, some decentralized exchanges like Curve, Canto Dex, and ApeX Pro are among the platforms with the lowest fees. However, compared with most centralized exchanges, many other large DEXs such as SushiSwap and Trader Joe are located in the high-fee segment.
Top 5 CEX And DEX With Lowest Fees (Maker / Taker)
OK, let’s cut to the chase! If it’s all about trading costs – which platforms offer you the best conditions?
Here are the respective top 5 for CEXs and DEXs.
Centralized Crypto Exchanges:
Bybit: 0.0% / 0.1%
Currency.com: 0.06% / 0.06%
Liquid: 0.0% / 0.15%
Hotbit: -0.05% / 0.2%
OKEx (OKX): 0.08% / 0.1%
Decentralized Crypto Exchanges:
Curve: 0.0% / 0.0%
Balancer: 0.0% / 0.0%
Canto Dex: 0.0% / 0.0%
ApeX Pro: 0.02% / 0.05%
SpookySwap: 0.2% / 0.2%
Final Words
When it comes to choosing the right trading platform, fees are of course an important consideration. In addition to fees, you should base your choice of a CEX or DEX on other aspects. For example, how anonymous do you want to be, and how secure is the exchange?
In any case, you should think carefully about whom you entrust your crypto to – after all, according to Coinmarketcap, there are over 1,000 crypto exchanges in total.
For those new to cryptocurrency, this post from investor.gov may help in navigating the risks involved.

Siyu Ren Heinrich
5 years of experience in crypto research of writing practical blockchain and crypto analysis on Medium.
MSc in Computer Science, BSc in Smart Engineering, and BSc in Economics and Statistics.
Michael has been active in the crypto community since 2017. He holds certifications from Duke University in decentralized finance (DeFi) and blockchain technology.
🍒 tasty reads


Aerodrome (AERO) For Beginners: The Ultimate 2024 Guide


Here’s How DEXTools (DEXT) Works in 2024

What Is Jasmy Coin and How Does It Work in 2024?


